Marine Diesel Engine Maintenance Schedule
Comprehensive guide to marine diesel engine maintenance schedules, including tasks, intervals, and MAN engine specifics for optimal performance.
Marine diesel engines are the heart of many vessels, delivering reliable power for recreational and commercial boating. Proper maintenance is critical to ensure longevity, efficiency, and safety. This guide provides a detailed marine diesel engine maintenance schedule, with a focus on general practices and specific considerations for MAN common rail engines. By adhering to a structured maintenance plan, boat owners can prevent costly repairs, extend engine life, and enjoy trouble-free operation. The article covers daily, periodic, and long-term maintenance tasks, factors affecting intervals, and the importance of a maintenance log, with specific insights into MAN engines’ unique requirements.
Why Marine Diesel Engine Maintenance Matters
Marine diesel engines operate in harsh environments, exposed to saltwater, high humidity, and varying temperatures. Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear, reduced fuel efficiency, and catastrophic failures. Regular upkeep ensures:
- Reliability: Prevents unexpected breakdowns during critical operations.
- Efficiency: Maintains optimal fuel consumption and performance.
- Longevity: Extends engine life, reducing replacement costs.
- Safety: Minimizes risks associated with engine failure at sea.
A well-maintained engine also enhances resale value and ensures compliance with manufacturer warranties. This guide outlines a comprehensive schedule, drawing from industry standards and manufacturer recommendations, including those from MAN and trusted sources like Diesel Services of America and SBMAR.
General Marine Diesel Engine Maintenance Schedule
The maintenance schedule for marine diesel engines varies by manufacturer, engine model, usage, and environmental conditions. Below is a detailed breakdown of tasks based on operating hours or time intervals. Always consult your engine’s manual for specific recommendations.
Daily or Every 8 Hours
Daily checks are quick but essential to catch issues early:
- Engine Oil Level: Check using the dipstick to ensure adequate lubrication.
- Visual Inspection: Look for leaks, loose components, or unusual noises.
- Coolant/Antifreeze Level: Verify levels in the header tank or overflow bottle.
- Belt Tension: Ensure belts for alternator, coolant, and raw water pumps are properly tensioned.
Every 50-100 Hours or Monthly
These tasks focus on maintaining critical systems:
- Change Engine Oil and Filter: Replace to prevent sludge buildup and ensure smooth operation.
- Check Drive Belt Tension and Condition: Inspect for wear, cracks, or glazing.
- Inspect for Leaks: Check fresh and seawater pumps for signs of leakage.
- Battery Maintenance: Verify electrolyte levels in starting batteries and clean terminals.
- Electric Fuel Pump Inspection: Ensure proper operation to maintain fuel delivery.
- Zinc Anodes: Check and replace if more than 50% eroded to prevent corrosion.
Every 200 Hours or Yearly
Annual maintenance ensures long-term reliability:
- Change Engine Oil and Filters: Replace oil and both oil and fuel filters.
- Replace Fuel Filter Cartridges: Ensure clean fuel delivery to prevent injector issues.
- Clean Fuel Pre-Filter and Drain Water: Remove contaminants from auxiliary fuel filters.
- Check Shaft Alignment: Verify alignment to reduce vibration and wear.
- Inspect Raw Water Impellers: Replace if worn to maintain cooling efficiency.
- Check Hose Clamps and Connections: Tighten or replace to prevent leaks.
- Inspect Belts and Hoses: Check for proper tension and signs of wear or leaks.
- Verify Engine Alarms and Instruments: Ensure all sensors and gauges function correctly.
- Check Oil and Coolant Levels: Top up as needed.
Every 250 Hours or Yearly
Additional tasks focus on air and exhaust systems:
- Replace Air Filters: Ensure proper airflow to maintain combustion efficiency.
- Inspect Turbocharger: Check for wear, oil leaks, or abnormal noise.
- Inspect Exhaust System: Look for leaks, corrosion, or blockages.
- Flush Seawater System: Use a descaling solution to remove marine growth and scale.
Every 400 Hours or Yearly
These tasks address deeper system maintenance:
- Change Crankcase Breather Filter: Prevent oil contamination and pressure buildup.
- Replace Zinc Anodes: Replace if significantly eroded to protect against galvanic corrosion.
Every 500 Hours or Every 2 Years
Biennial tasks focus on cooling and valve systems:
- Change Coolant and Flush Cooling System: Replace coolant to maintain thermal efficiency.
- Check Valve Clearance: Adjust to ensure optimal engine performance.
- Flush Seawater Passages: Remove scale and debris to maintain cooling efficiency.
Every 800 Hours or Every 2 Years
These tasks address critical components:
- Inspect Aftercooler Core: Clean to maintain air intake efficiency.
- Test Engine Protective Devices: Verify shutdown systems and alarms function correctly.
- Clean and Inspect Magnetic Pickups: Ensure accurate sensor operation.
- Inspect Turbocharger: Perform a detailed inspection for wear or damage.
Every 1000 Hours or Every 4-5 Years
Long-term maintenance ensures injector performance:
- Check Fuel Injector Spray Patterns: Test and clean to maintain fuel efficiency and power output.
Maintenance Task Table
Below is a summarized table of maintenance tasks and intervals for quick reference:
| Interval | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Daily/8 Hours | Check oil, coolant, belts; visual inspection |
| 50-100 Hours/Monthly | Change oil/filter, check belts, inspect pumps, battery, zinc anodes |
| 200 Hours/Yearly | Change oil/filters, fuel filters, check alignment, impellers, hoses, alarms |
| 250 Hours/Yearly | Replace air filters, inspect turbo/exhaust, flush seawater system |
| 400 Hours/Yearly | Change oil/filters, crankcase breather, air filter, inspect zinc anodes |
| 500 Hours/2 Years | Change coolant, flush cooling system, check valve clearance |
| 800 Hours/2 Years | Inspect aftercooler, test protective devices, clean magnetic pickups |
| 1000 Hours/4-5 Years | Check fuel injector spray patterns |
Factors Affecting Maintenance Intervals
Several factors influence the frequency and type of maintenance required:
- Engine Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Always prioritize the schedule in the engine manual, as specifications vary by brand and model.
- Operating Environment: Saltwater accelerates corrosion, requiring more frequent anode and cooling system checks.
- Usage Patterns: Heavy use (e.g., commercial vessels) demands shorter intervals than recreational use.
- Local Water Conditions: High sediment or marine growth may necessitate more frequent impeller and strainer maintenance.
Adjusting the schedule based on these factors ensures optimal performance and prevents premature wear.
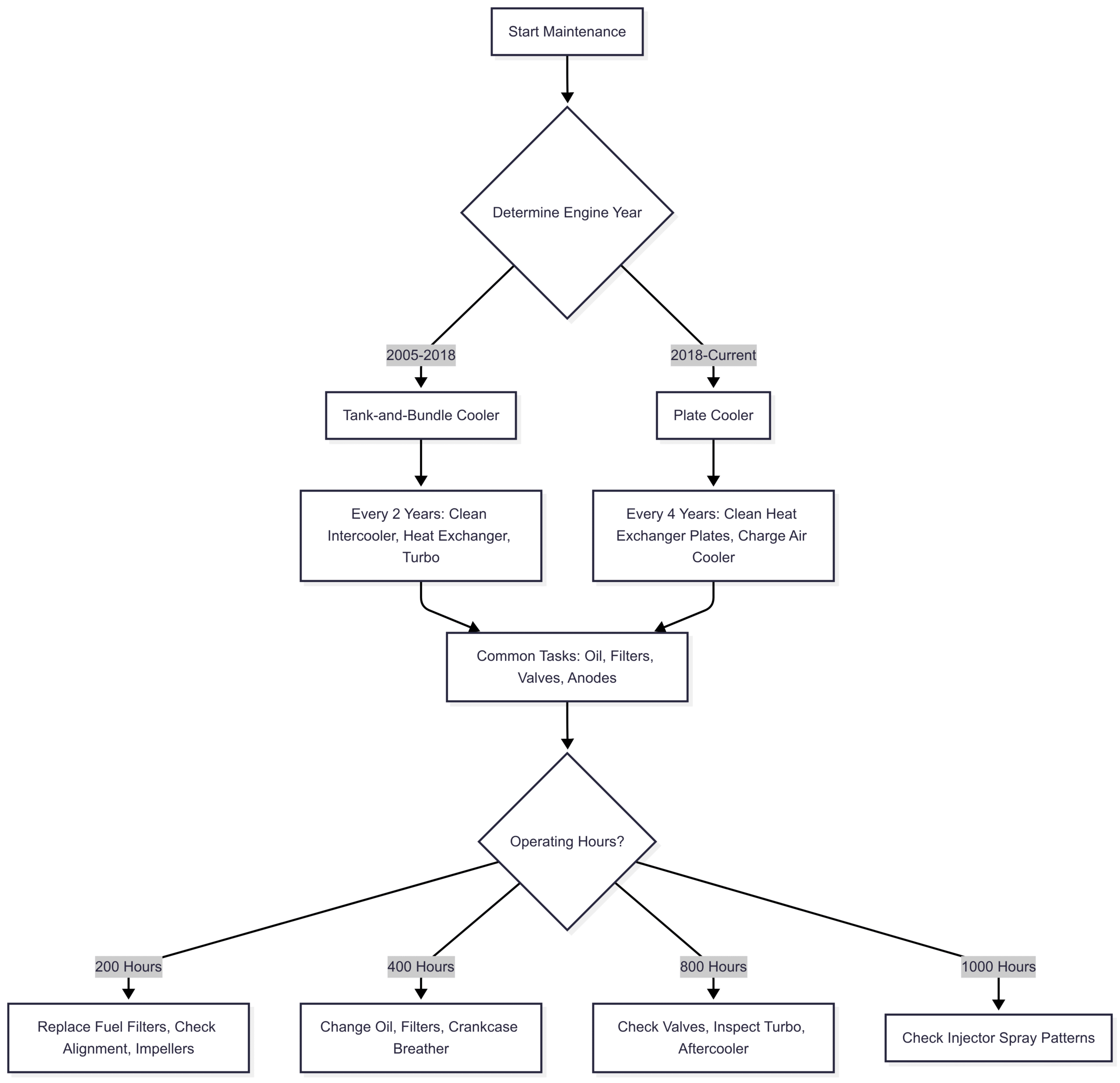
MAN Common Rail Marine Diesel Engines: A Focused Maintenance Plan
MAN common rail diesel engines, introduced in recreational marine applications in 2005, are renowned for their advanced technology, fuel efficiency, and low emissions. Available in inline 6, V8, V10, and V12 configurations, they deliver 600 to 2000 horsepower with excellent power-to-weight ratios, minimal vibration, and low noise. This section outlines a tailored maintenance plan for MAN engines, addressing misconceptions and highlighting updates, particularly the shift from tank-and-bundle to plate cooling systems in 2018.
MAN Engine Overview
MAN engines are a pinnacle of German engineering, offering:
- Fuel Efficiency: Common rail injection optimizes fuel delivery, reducing consumption.
- Performance: High torque and power across a wide RPM range.
- Low Emissions: Reduced smoke and noise compared to traditional diesels.
- Durability: Robust construction for marine environments.
A common misconception is that MAN engines require more intensive and costly maintenance. However, modern iterations, particularly the V8 and V12 models post-2018, have simplified cooling systems, reducing service frequency compared to competitors like Caterpillar (CAT).
Key Maintenance Intervals for MAN Engines
The following schedule applies to all MAN common rail engines, with distinctions for pre- and post-2018 cooling systems.
Every 200 Hours or Yearly
- Fuel System:
- Replace fuel filter cartridges (use 10-micron primary and 2-micron secondary filters).
- Clean fuel pre-filter and drain water from auxiliary filters.
- Mechanical Checks:
- Verify shaft alignment to reduce vibration.
- Inspect raw water impellers for wear.
- Check hose clamps, pipe connections, and bolts for tightness.
- Adjust or replace belts as needed.
- System Inspections:
- Check hoses for leaks.
- Verify engine alarms and instruments.
- Monitor oil and coolant levels.
Every 400 Hours or Yearly
- Lubrication and Filtration:
- Change engine oil and filters.
- Replace crankcase breather filter element.
- Change air filter to ensure proper combustion.
- Corrosion Protection:
- Inspect and replace zinc anodes if significantly eroded.
Every 400, 800, and Every 800 Hours Thereafter
- Valve Clearance: Check and adjust to maintain engine efficiency.
Every 2 Years (2005-2018 Tank-and-Bundle Coolers)
- Cooling System:
- Replace valve caps on the expansion tank.
- Clean and flush intercooler and charge-air pipes.
- Clean heat exchanger pipe cluster.
- Turbocharger:
- Clean and inspect for wear or oil leaks.
Every 4 Years (2018-Current Plate Coolers)
- Cooling System:
- Remove and clean heat exchanger plates.
- Clean charge air cooler.
- General:
- Change engine coolant.
- Replace all hoses to prevent leaks.
Cooling System Evolution
In 2018, MAN transitioned from tank-and-bundle to plate cooling systems, significantly reducing maintenance demands:
- Tank-and-Bundle (2005-2018): Required cleaning and maintenance every 2 years due to complex pipe clusters prone to scaling and corrosion.
- Plate Coolers (2018-Current): More durable, requiring service only every 4 years, with simpler disassembly and cleaning.
This change reduced maintenance costs and downtime, making MAN engines competitive with or less demanding than brands like CAT.
Maintenance Flowchart
Below is a Mermaid flowchart illustrating the decision-making process for MAN engine maintenance:
Service Considerations
- Basic Maintenance: Oil changes and filter replacements can be handled by any competent diesel mechanic.
- Complex Repairs: Warranty work or intricate issues (e.g., injector or turbocharger repairs) require a certified MAN technician. MAN’s global dealer network ensures accessibility in most boating regions, though remote areas may require travel arrangements.
- Reliability: With proper maintenance, MAN engines are highly reliable, with rare major failures.
For detailed schedules, download MAN’s official maintenance plans:
The Importance of a Maintenance Log
A maintenance log is a critical tool for tracking engine health and preventing issues. It serves four primary functions:
- Early Warning: Identifies developing problems, such as slow leaks or performance changes.
- Performance Tracking: Records changes in engine behavior, aiding diagnostics.
- Service History: Documents tasks performed, parts replaced, and service providers.
- System Overview: Provides a comprehensive history for troubleshooting and resale.
How to Create a Maintenance Log
Use a simple notebook with four columns:
| Date/Time | Item | Notes | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-07-26 | Oil Filter | Replaced with OEM filter | Check for leaks next week |
| 2025-07-26 | Raw Water Impeller | Inspected, slight wear | Replace in 50 hours |
Regular entries ensure no task is overlooked and provide valuable data for technicians.
Six Common Faults in Raw Water Pump Impellers
The raw water pump impeller is critical for cooling and prone to wear. Inspect for:
- Cracks or Tears: Indicate material fatigue; replace immediately.
- Missing Vanes: Reduce cooling efficiency; replace impeller.
- Hardened or Brittle Rubber: Signals overheating or age; replace.
- Deformed Vanes: Caused by prolonged dry running; replace.
- Worn Hub: Prevents proper pump operation; replace impeller.
- Corrosion: Check pump housing for pitting or wear; repair or replace.
Regular inspection prevents overheating and costly repairs.
Dipstick Diagnostics: Five Key Checks
The engine dipstick provides insights into engine health:
- Oil Level: Low levels indicate leaks or consumption; top up and investigate.
- Oil Color: Black oil is normal; milky oil suggests coolant contamination.
- Oil Consistency: Thick or gritty oil indicates sludge or wear; change immediately.
- Metal Particles: Shiny flecks suggest internal wear; consult a technician.
- Odor: Burnt or fuel-like smells indicate combustion issues; investigate further.
Saildrive Maintenance
Saildrives, common in smaller vessels, require specific attention:
- Daily: Check gear oil level.
- Weekly: Scrape propeller and shaft; burp air from gear oil dipstick.
- Monthly: Inspect paint protection and clean raw water intake.
- 3 Months: Check transmission coupling and stern gland.
- 100-250 Hours: Change gear oil in the lower unit.
- 6 Months: Inspect propeller shaft anode.
- Yearly: Inspect rubber fairing flange, sealing ring, and water sensor; service propeller.
Cost and Specifications
Typical Maintenance Costs
Costs vary by region, engine size, and labor rates. Approximate ranges:
| Task | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Oil and Filter Change | $100-$300 |
| Fuel Filter Replacement | $50-$150 |
| Impeller Replacement | $50-$200 |
| Coolant Change (2-4 Years) | $200-$500 |
| Valve Clearance Adjustment | $300-$600 |
| Turbocharger Inspection | $400-$800 |
MAN Engine Specifications
| Model | Horsepower | Configuration | Cooling System (Post-2018) |
|---|---|---|---|
| i6-800 | 800 HP | Inline 6 | Plate Cooler |
| V8-1000 | 1000 HP | V8 | Plate Cooler |
| V12-2000 | 2000 HP | V12 | Plate Cooler |
Best Practices for Marine Diesel Maintenance
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the engine manual’s schedule.
- Use Quality Parts: OEM or high-quality aftermarket components ensure reliability.
- Cultivate Vigilance: Regularly inspect for unusual sounds, leaks, or performance changes.
- Maintain a Log: Document all maintenance for reference and resale value.
- Know Your Boat: Verify installations and configurations to avoid issues from improper setups.
- Invest in Training: Basic diesel maintenance courses empower owners to handle routine tasks.
Conclusion
A structured marine diesel engine maintenance schedule is essential for reliability, efficiency, and longevity. By following daily, periodic, and long-term tasks, boat owners can prevent issues and enjoy seamless operation. MAN common rail engines, with their advanced technology and simplified cooling systems post-2018, offer competitive maintenance intervals and exceptional performance. A detailed maintenance log, regular inspections, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines ensure your engine remains in top condition. Invest time and quality components now to avoid costly repairs later, and enjoy your vessel for years to come.
Happy Boating!
Share Marine Diesel Engine Maintenance Schedule with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read An Introduction to Ship Automation and Control Systems until we meet in the next article.