Troubleshooting Marine Diesel Engines the quick & easy way
Master marine diesel engine troubleshooting with our comprehensive guide. Diagnose and fix common issues like overheating, power loss, and smoke for smooth sailing.
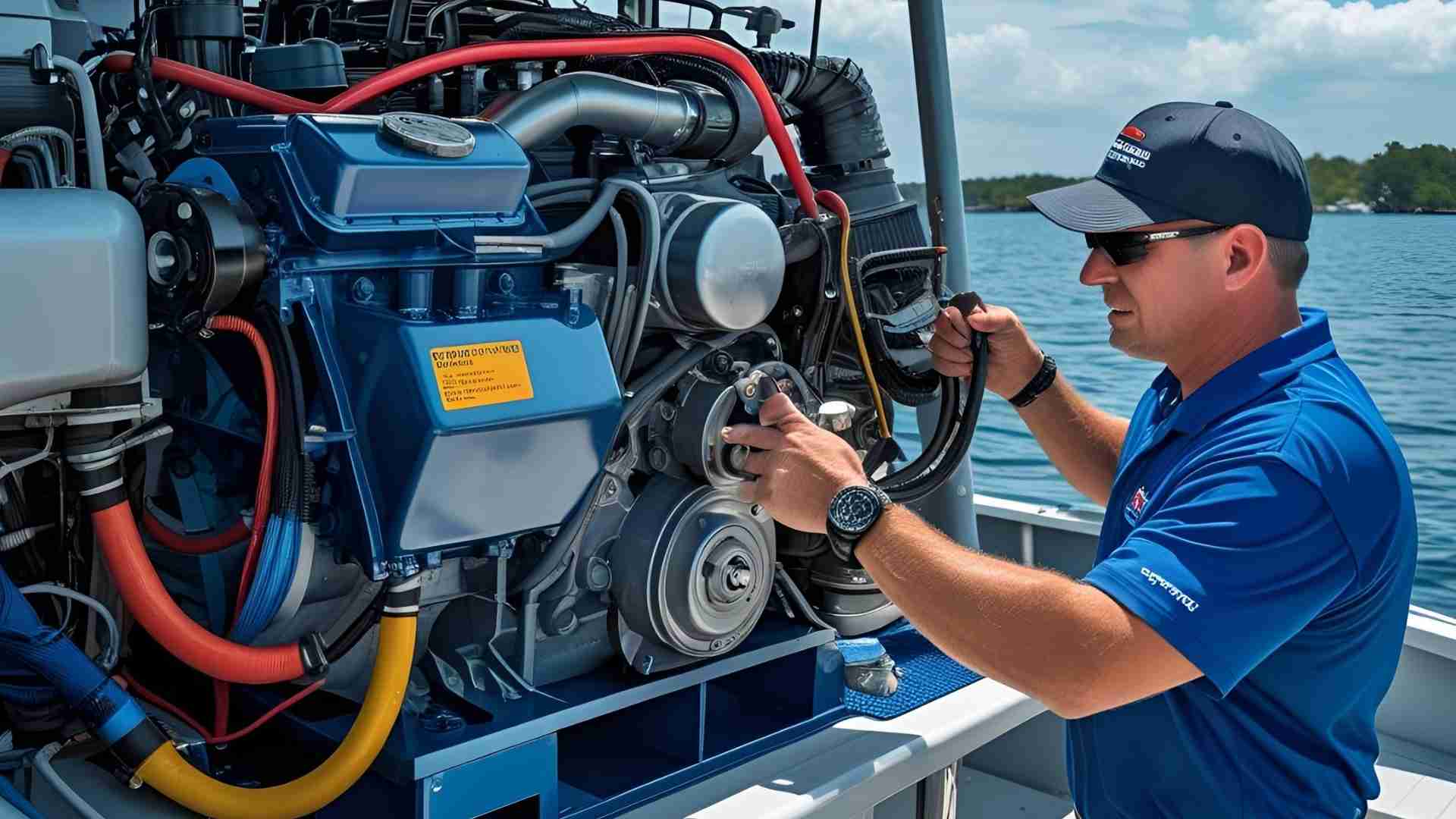
Marine diesel engines are the reliable workhorses of the seas, powering vessels with efficiency and durability. However, even the most robust engines can encounter issues that disrupt voyages. From overheating to power loss, diagnosing and resolving problems quickly is critical to minimizing downtime and ensuring safe, sustainable operation. This comprehensive guide provides boat owners and marine professionals with a systematic approach to troubleshooting marine diesel engines, emphasizing proactive maintenance, practical solutions, and when to seek professional help.
Understanding Marine Diesel Engines
Marine diesel engines operate on the principle of compression ignition, where atomized diesel fuel ignites under high pressure within cylinders, driving pistons to produce rotary motion via the crankshaft. This four-stroke cycle—intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust—relies on the seamless interaction of fuel, air, lubrication, cooling, and electrical systems. Any disruption in these systems can lead to performance issues, making a structured troubleshooting process essential.
The marine environment poses unique challenges, including exposure to saltwater, humidity, and constant vibration, which can accelerate wear and tear. Regular maintenance and early detection of problems are vital to extending engine life and preventing costly repairs. By understanding common issues and their solutions, boat owners can keep their engines running smoothly and contribute to sustainable boating practices by reducing emissions and fuel waste.
Common Marine Diesel Engine Problems
Marine diesel engines encounter a range of issues, each with distinct symptoms and causes. Below is a detailed look at the most frequent problems, their causes, and actionable solutions.
1. Engine Won’t Start
Symptoms: The engine cranks but fails to start, or there’s no response when the key is turned.
Causes:
- Fuel Supply Issues: Empty tank, closed fuel valve, or water contamination.
- Electrical Problems: Dead battery, corroded connections, or faulty starter solenoid.
- Air in Fuel System: Air locks preventing fuel delivery to injectors.
Solutions:
- Check the fuel tank level and ensure the shut-off valve is open.
- Inspect battery terminals for corrosion and verify voltage (12.4V or higher for a fully charged battery).
- Bleed the fuel system to remove air, starting at the primary filter and moving to the injectors.
- Test the starter motor and solenoid for proper function.
2. Overheating
Symptoms: High temperature gauge readings, steam from the exhaust, or reduced power.
Causes:
- Cooling System Blockages: Clogged seawater strainer, damaged impeller, or salt buildup in passages.
- Low Coolant Levels: Insufficient freshwater/antifreeze mix in indirect cooling systems.
- Thermostat Failure: Stuck thermostat restricting coolant flow.
Solutions:
- Verify seawater flow (e.g., Beta 35 engines should output ~16 liters/min at 1500 RPM).
- Clean the seawater strainer and inspect the impeller for missing vanes or wear; replace if needed.
- Check coolant levels and top up with the correct antifreeze mixture.
- Remove and test the thermostat; run the engine without it temporarily if necessary.
- Flush the heat exchanger to remove salt or debris.
3. Loss of Power
Symptoms: Engine struggles to reach full RPM, stalls, or runs unevenly.
Causes:
- Fuel System Issues: Clogged filters, contaminated fuel, or faulty injectors.
- Air Intake Restrictions: Dirty air filters or blocked engine compartment vents.
- Turbocharger Problems: Worn or obstructed turbo (if equipped).
Solutions:
- Replace clogged fuel filters and drain water from the fuel tank or separator.
- Clean or replace air filters; ensure vents are unobstructed.
- Inspect the turbocharger for damage or blockages; consult a professional for repairs.
4. Excessive Smoke
Symptoms: Black, blue, or white smoke from the exhaust.
Causes:
- Black Smoke: Incomplete combustion due to dirty air filters, faulty injectors, or turbo issues.
- Blue Smoke: Oil burning from worn piston rings or valve seals.
- White Smoke: Water in the fuel or a failing head gasket.
Solutions:
- For black smoke, clean or replace air filters and have injectors serviced.
- For blue smoke, check oil levels and inspect for internal engine wear; professional diagnosis may be needed.
- For white smoke, drain water from the fuel system and check the head gasket.
5. Electrical System Issues
Symptoms: Starter motor failure, dim gauges, or battery not charging.
Causes:
- Battery Issues: Low voltage, corroded terminals, or loose connections.
- Alternator Failure: Worn drive belt or faulty alternator.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring.
Solutions:
- Clean and tighten battery terminals; grease to prevent corrosion.
- Test battery voltage (should be ~12.6V when fully charged) and replace if faulty.
- Check alternator belt tension (~1cm play) and replace if worn.
- Inspect wiring for damage and ensure secure connections.
6. Lubrication System Problems
Symptoms: Low oil pressure warning, unusual noises, or oil leaks.
Causes:
- Low Oil Levels: Insufficient oil or overfilling.
- Contaminated Oil: Water or fuel in the oil, indicated by froth or discoloration.
- Oil Filter Issues: Clogged or improperly installed filter.
Solutions:
- Check oil levels with the dipstick and top up with the correct oil type.
- Inspect oil for contamination; change oil and filter if needed.
- Ensure the oil filter is hand-tight and undamaged.
7. Mechanical Issues
Symptoms: Excessive vibration, unusual noises, or propeller shaft not turning.
Causes:
- Propeller Fouling: Entangled ropes or marine growth.
- Engine Mounts: Loose or worn mounts causing misalignment.
- Gearbox Issues: Low oil or faulty gear engagement.
Solutions:
- Inspect and clear the propeller of debris; attempt reversing at low speed.
- Tighten or replace loose engine mounts.
- Check gearbox oil levels and cable connections; consult a professional for internal issues.
8. Exhaust System Issues
Symptoms: Backpressure, overheating, or water in the exhaust.
Causes:
- Blockages: Carbon buildup or damaged exhaust elbow.
- Ventilation Issues: Poorly ventilated engine compartment.
Solutions:
- Inspect the exhaust system for blockages and ensure the elbow is intact.
- Verify proper ventilation in the engine compartment.
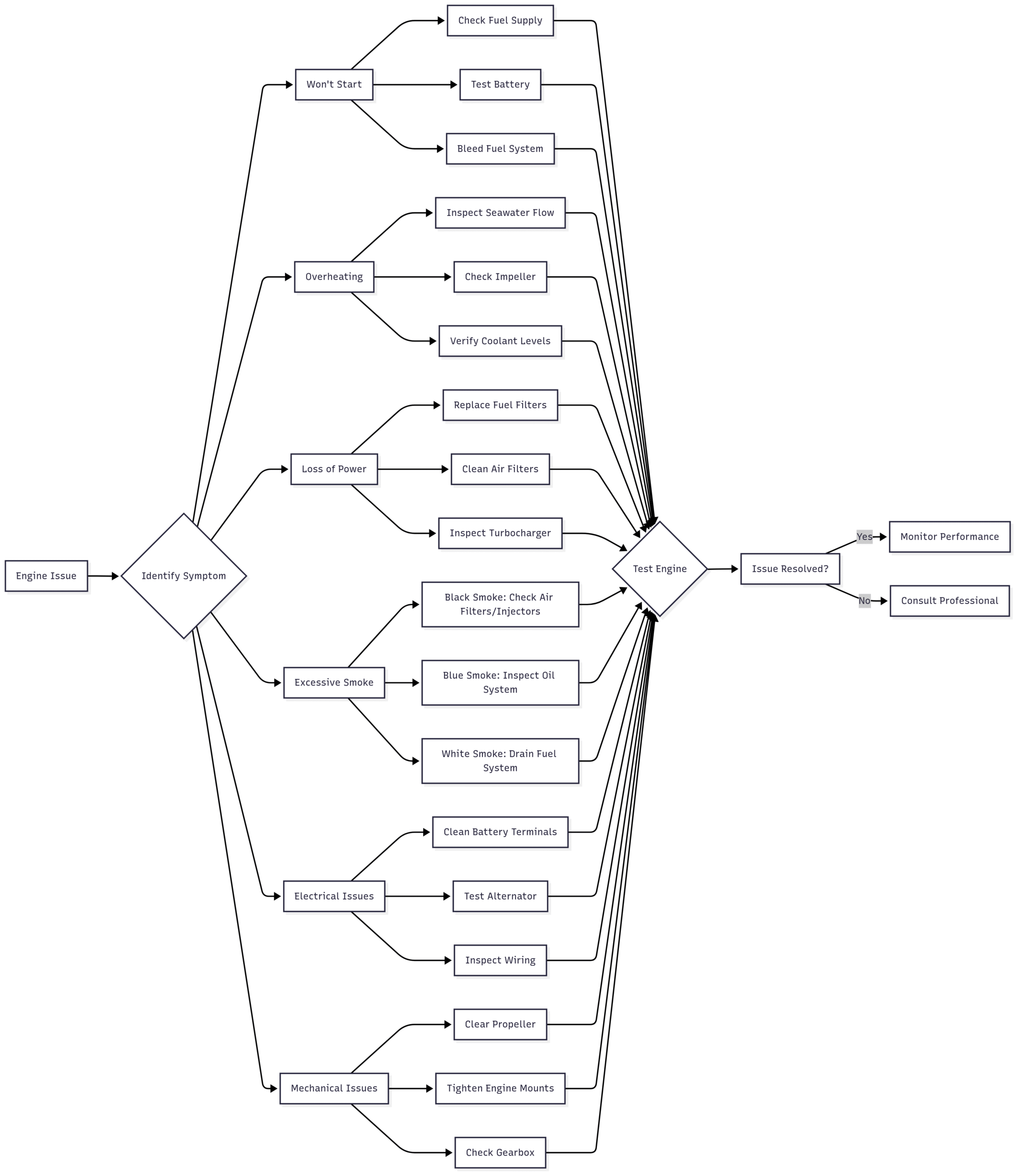
Troubleshooting Process: A Step-by-Step Approach
Effective troubleshooting requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve issues. Below is a streamlined process to diagnose marine diesel engine problems:
- Identify Symptoms: Note specific symptoms like failure to start, overheating, or smoke.
- Visual Inspection: Check for leaks, corrosion, or damaged components.
- Systematic Checks:
- Fuel System: Verify fuel levels, check for leaks, and bleed air from the system.
- Cooling System: Ensure seawater flow, inspect the impeller, and check coolant levels.
- Electrical System: Test battery voltage and inspect connections.
- Lubrication System: Check oil levels and condition.
- Mechanical Components: Inspect propeller, mounts, and gearbox.
- Test and Monitor: After addressing potential issues, test the engine and monitor performance.
- Seek Professional Help: For complex issues, consult a certified marine technician.
Chart: Troubleshooting Workflow
Preventive Maintenance: The Key to Reliability
Preventive maintenance is the cornerstone of marine diesel engine longevity. Regular checks and timely interventions can prevent most issues. Below is a maintenance schedule and key tasks:
Daily Checks
- Engine Oil Level: Ensure it’s within the dipstick’s marked range.
- Coolant Level: Verify adequate levels in indirect cooling systems.
- Fuel System: Inspect for leaks and ensure clean fuel.
- Bilge Pumps: Confirm functionality to manage water ingress.
- Battery Condition: Check charge and connections.
Pre-Voyage Checks
- Drive Belts: Verify tension (~1cm play) and condition.
- Seawater Strainer: Clean to ensure proper cooling water flow.
- Visual Inspection: Look for loose components or leaks.
Routine Maintenance
| Task | Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Oil and Filter Change | Every 100-200 hours or annually | Use manufacturer-specified oil; replace spin-on or cartridge filters. |
| Fuel Filter Replacement | Every 200 hours or annually | Replace primary and secondary filters; carry spares. |
| Cooling System Flush | Annually | Flush seawater and freshwater systems; check for corrosion. |
| Impeller Inspection | Every 200 hours or annually | Replace if worn or damaged; keep spares onboard. |
| Anode Inspection | Every 6 months | Replace sacrificial anodes to prevent galvanic corrosion. |
| Turbocharger Check | Annually | Inspect for wear or obstructions; professional service may be needed. |
| Valve Clearance Check | Per manufacturer | Adjust to specifications to maintain performance. |
Fuel Quality
Use high-quality, clean diesel fuel and regularly drain water and sediment from tanks and filters. A fuel filter funnel can prevent contamination during refueling.
Electrical System
Keep battery terminals clean and greased. Test alternator output (~14V when running) and carry spare fuses for quick replacements.
Cooling System
Ensure proper seawater flow and check the impeller annually. Use a 50/50 freshwater/antifreeze mix for indirect cooling systems.
Exhaust System
Inspect for blockages and ensure proper ventilation to prevent backpressure.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For persistent or complex issues, advanced diagnostics may be required:
- Compression Test: Measures cylinder pressure (ideal range: 300-500 PSI). Low readings indicate worn piston rings or valves.
- Fuel Injection Timing: Incorrect timing can cause power loss or smoke. Requires professional adjustment.
- Diagnostic Scanners: Modern engines may have control units that store error codes, accessible via diagnostic tools.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many issues can be resolved with basic tools and knowledge, some require specialized skills:
- Internal engine repairs (e.g., piston or crankshaft issues).
- Turbocharger servicing.
- Fuel injection system calibration.
- Major electrical or gearbox repairs.
Certified marine technicians, such as those at RPM Diesel Company, offer expertise and access to hard-to-find parts. For complex issues, visit a factory-authorized service center.
Specifications and Costs of Common Components
| Component | Typical Specifications | Approx. Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Filter (CAV 296) | M14x1.5 BSP threads, aluminum | $10-$20 |
| Impeller | Varies by engine (e.g., Beta 35, Yanmar 2GM20) | $20-$50 |
| Oil Filter | Spin-on or cartridge type | $10-$25 |
| Antifreeze Tester | Propylene glycol, disc type | $15-$30 |
| Drive Belt | V-belt, ~1cm play | $10-$20 |
| Battery (Marine) | 12V, 800-1000 CCA | $100-$200 |
Note: Prices vary by region and supplier. Check with manufacturers like Beta Marine or Yanmar for exact specifications.
Sustainability and Marine Diesel Engines
Proper maintenance not only ensures reliability but also reduces environmental impact. Efficient engines burn less fuel, lowering emissions. Regular filter replacements and clean fuel use prevent excessive smoke, contributing to cleaner waterways. Sacrificial anodes protect against corrosion, reducing the need for frequent part replacements and minimizing waste.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting marine diesel engines requires a blend of observation, routine maintenance, and practical know-how. By addressing common issues like overheating, power loss, and smoke through systematic checks, boat owners can ensure smooth, reliable voyages. Regular maintenance—daily inspections, filter changes, and system flushes—prevents most problems, while advanced diagnostics and professional help tackle complex issues. Equipped with this guide, you can confidently maintain your marine diesel engine, ensuring it remains the reliable heart of your vessel while contributing to sustainable boating practices.
For further assistance or professional servicing, contact experts like RPM Diesel Company, who offer comprehensive marine engine solutions worldwide.
Happy Boating!
Share Troubleshooting Marine Diesel Engines the quick & easy way with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read Checklist – Before Departure – Engine Room until we meet in the next article.