STCW-Compliant VR Maritime Training
Explore STCW-compliant VR maritime training, revolutionizing seafarer education with immersive safety drills, engine simulations, and IMO-aligned competency learning.
The maritime industry, a cornerstone of global trade, demands highly skilled professionals capable of handling complex and high-risk situations at sea. From extinguishing engine room fires to navigating lifeboat drills, seafarers must be prepared for emergencies that test their competence and composure. Traditionally, maritime training has relied on physical simulators, live drills, and classroom instruction to meet the Standards of Training, Certification, and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW) set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). However, these methods often come with high costs, logistical challenges, and safety risks.
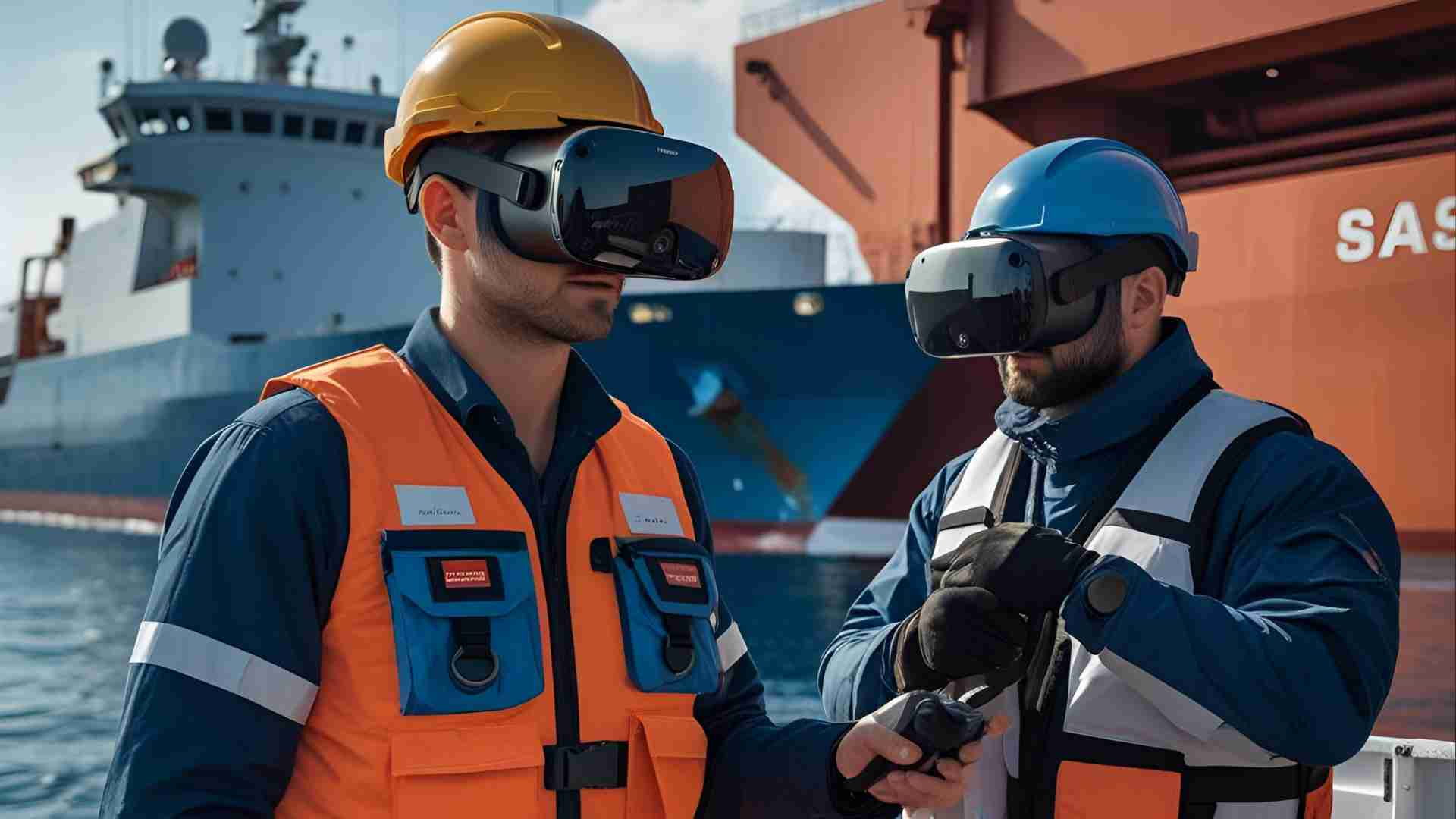
Enter STCW-compliant Virtual Reality (VR) maritime training—a transformative approach that leverages immersive technology to simulate realistic scenarios, ensuring seafarers meet global safety and competency standards. VR training allows mariners to practice critical skills in a safe, repeatable, and cost-effective environment, revolutionizing how maritime education is delivered. This article explores the technology, applications, benefits, and future of STCW-compliant VR training, offering insights for maritime students, ship officers, educators, and shipping companies.
What Is STCW-Compliant VR Maritime Training?
STCW-compliant VR maritime training uses virtual reality to deliver immersive, interactive learning experiences that align with the IMO’s STCW Convention. Established in 1978 and amended in 1995 and 2010, the STCW Convention sets minimum standards for seafarer training, certification, and watchkeeping to ensure safety, protect property, and safeguard the marine environment. VR training platforms simulate STCW-approved modules, enabling trainees to develop essential knowledge, skills, and proficiencies (KUPs) in realistic, scenario-based environments.
Key Components of STCW Training
The STCW Basic Training course, a mandatory requirement for all seafarers, includes five core modules:
- Basic Firefighting: Covers fire identification, prevention, detection, and firefighting techniques, including search and rescue (SAR) in smoke-filled environments.
- Personal Survival Techniques (PST): Teaches survival skills such as abandoning ship, deploying life rafts, and operating life-saving equipment.
- Personal Safety and Social Responsibilities (PSSR): Focuses on workplace relationships, safe work environments, and personal care.
- Elementary First Aid and CPR: Provides training in basic medical first aid and CPR for maritime-specific emergencies.
- Proficiency in Security Awareness: Addresses security protocols for seafarers on commercial vessels.
VR training enhances these modules by immersing trainees in 3D environments where they can practice skills like extinguishing fires, launching life rafts, or performing CPR without real-world risks. Advanced modules, such as Engine Room Resource Management (ERRM), Bridge Watchkeeping, and Proficiency in Fast Rescue Boats, are also supported by VR platforms.
How VR Aligns with STCW
VR training programs are designed to meet IMO model course requirements and are delivered by certified institutions like Maritime Institute of Technology and Graduate Studies (MITAGS) or through partnerships with technology providers like Kongsberg Digital and Ocean Management Systems (OMS). These programs ensure compliance with STCW competencies, making them valid for certifications and refreshers.
Why VR Training Matters in the Maritime Industry
Traditional maritime training faces several challenges:
- High Costs: Physical simulators, live fire drills, and shipboard training require significant investment in equipment and facilities.
- Safety Risks: Real-life drills, such as firefighting or lifeboat launches, can lead to injuries if not carefully managed.
- Limited Access: Cadets in remote regions or those without access to advanced training centers struggle to complete mandatory training.
- Inconsistent Quality: Training quality varies across global institutions, affecting competency standards.
VR training addresses these issues by offering:
- Immersive Learning: Trainees engage in hands-on practice within realistic 3D environments, building muscle memory and confidence.
- Safe Repetition: High-risk scenarios, such as engine fires or man-overboard drills, can be practiced repeatedly without danger.
- Scalability and Portability: VR headsets and cloud-based software can be deployed globally, requiring minimal infrastructure.
- Real-Time Feedback: AI-driven analytics monitor trainee performance, providing instant feedback and detailed competency assessments.
Evidence of Effectiveness
A study by the World Maritime University (WMU) found that VR-enhanced training improves knowledge retention by up to 75%, compared to just 10% for traditional lectures. This is attributed to the experiential nature of VR, which engages multiple senses and reinforces learning through repetition.
Key Applications of STCW-Compliant VR Training
VR training covers a wide range of STCW modules, addressing both basic and advanced competencies. Below are the primary applications:
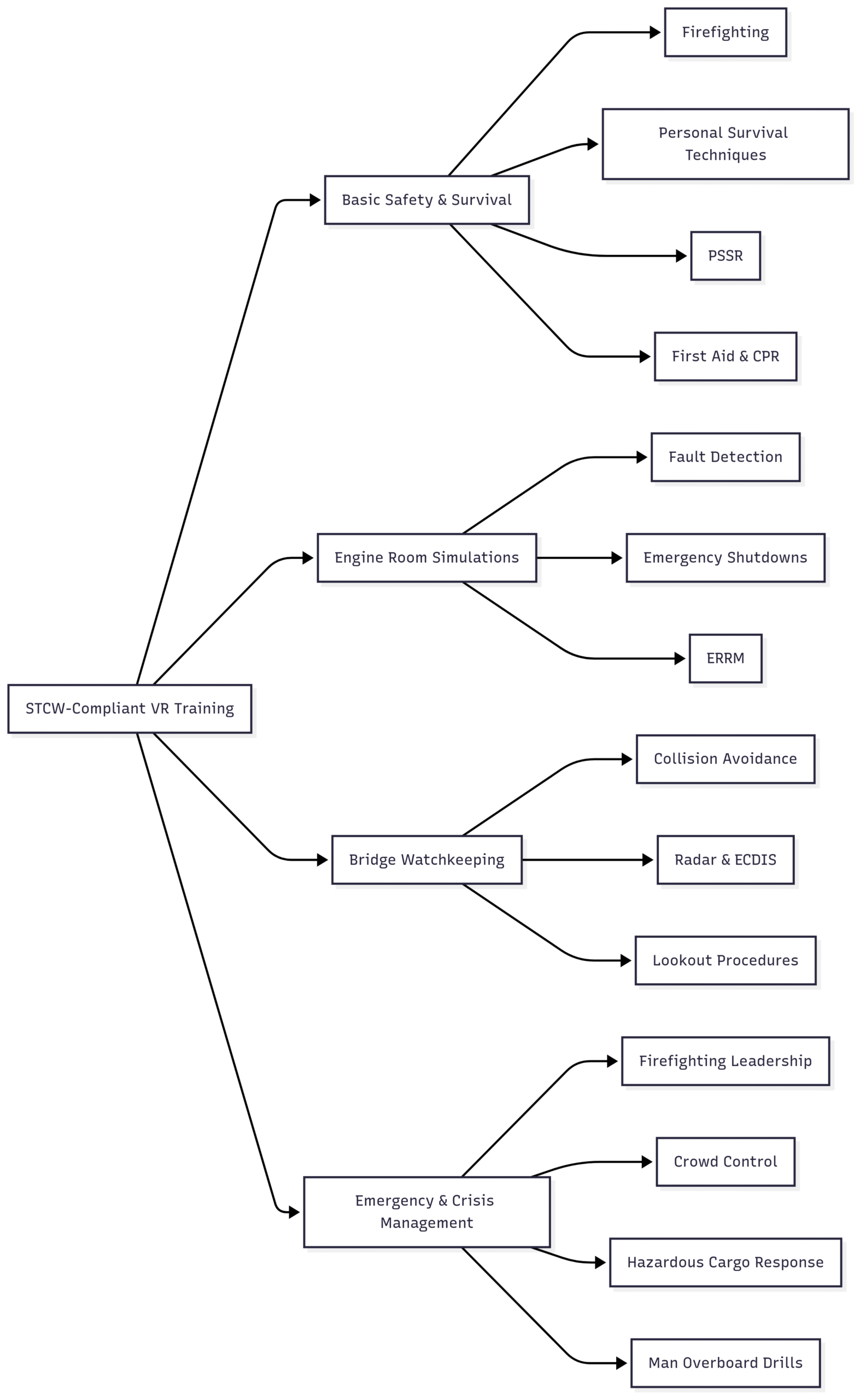
1. Basic Safety and Survival Techniques
VR simulates critical safety scenarios, allowing trainees to practice:
- Fire Response: Handling Class A, B, and electrical fires, using extinguishers, and navigating smoke-filled compartments.
- Abandon Ship Drills: Deploying life rafts, using rescue equipment, and surviving cold water immersion.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Proper use of PPE in hazardous environments.
- Survival Exercises: Techniques for staying afloat and signaling for rescue.
Example: Seably’s STCW-compliant VR modules allow trainees to practice life raft deployment in a virtual storm, enhancing decision-making under pressure.
2. Engine Room Simulations
VR replicates engine room environments for training in:
- Fault Detection: Identifying issues in pumps, generators, and boilers.
- Emergency Procedures: Managing fuel systems, executing shutdowns, and responding to alarms.
- Team Coordination: Practicing Engine Room Resource Management (ERRM) protocols.
Example: Kongsberg Digital’s K-Sim VR platform simulates engine room faults, enabling trainees to diagnose and resolve issues in real time.
3. Bridge Watchkeeping and Navigation
VR supports bridge operations training, including:
- Collision Avoidance: Applying International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs) in simulated traffic scenarios.
- Radar and ECDIS: Operating Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems in adverse weather conditions.
- Lookout Procedures: Practicing watchkeeping and handover responsibilities.
Example: Trainees can simulate navigating a vessel through dense fog using VR, improving situational awareness and decision-making.
4. Emergency and Crisis Management
VR prepares seafarers for high-stakes scenarios, such as:
- Firefighting Leadership: Coordinating firefighting teams during engine or accommodation fires.
- Crowd Control: Managing passengers during evacuations on cruise ships.
- Hazardous Cargo Response: Handling spills or leaks of dangerous goods.
- Man Overboard Drills: Coordinating search-and-rescue operations.
Example: OMS-VR’s immersive scenarios allow trainees to practice man-overboard recovery, enhancing leadership and communication skills.
Chart: VR Training Modules
Below is a visual representation of key STCW-compliant VR training modules:
Benefits of STCW-Compliant VR Training
VR training offers significant advantages over traditional methods, as outlined in the table below:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Realistic Scenario Repetition | Builds muscle memory and improves decision-making under pressure. |
| Standardized Training Quality | Ensures consistent STCW compliance across global training centers. |
| Reduced Operational Costs | Eliminates the need for expensive physical simulators or shipboard visits. |
| Remote Learning Capabilities | Enables training access for seafarers in remote or pandemic-affected areas. |
| Improved Record Keeping | Generates performance data for audits and STCW certification documentation. |
Additional Benefits
- Improved Knowledge Retention: VR’s immersive nature enhances recall compared to traditional methods.
- Reduced Training Time: Competency can be achieved faster through repeated practice in virtual environments.
- Increased Engagement: Interactive scenarios motivate trainees and maintain focus.
- Better Preparation: VR simulates real-world challenges, preparing seafarers for emergencies.
Instructor’s Tip: Many VR platforms integrate with Learning Management Systems (LMS), enabling trainers to track progress, generate STCW documentation, and provide personalized feedback.
STCW Training Tiers: Original, Refresher, and Revalidation
Maintaining an STCW Basic Training endorsement requires seafarers to revisit skills every five years as part of Merchant Mariner Credential (MMC) renewal. The three tiers of STCW Basic Training are:
| Course Type | Description | Duration | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Training | Original certification covering all five modules (Firefighting, PST, PSSR, First Aid, Security Awareness). | 5 days | New seafarers seeking initial STCW endorsement. |
| Basic Training Refresher | Required for mariners with less than 360 days of sea service in the past 5 years, revisiting all modules. | 3 days | Mariners not sailing regularly, needing updated proficiency. |
| Basic Training Revalidation | For mariners with 360+ days of sea service, focusing on Firefighting and PST. | 2 days | Active mariners maintaining STCW endorsement through regular safety drills. |
Note: Mariners unsure about their training needs should consult advisors at institutions like MITAGS to determine the appropriate course.
Pricing and Accessibility
Course costs vary based on type, duration, and location. Below is an estimated cost range for STCW-compliant courses, including VR-based options where applicable:
| Course | Duration | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Training (Original) | 5 days | $1,200–$2,500 | Includes all five modules; VR options may lower costs at some institutions. |
| Basic Training Refresher | 3 days | $800–$1,500 | For mariners with limited sea time; VR reduces facility costs. |
| Basic Training Revalidation | 2 days | $600–$1,200 | For active mariners; VR enhances efficiency. |
| First Aid and CPR | 1 day | $200–$500 | Often offered as a standalone VR module. |
| Personal Safety and Social Responsibilities | 1 day | $150–$400 | Classroom-based, with VR simulations for practical scenarios. |
Note: Costs vary by institution (e.g., MITAGS, MPT) and location (e.g., Seattle, Maryland). Some programs, like those for Pacific Northwest fishing crews, may be free through grants (contact [email protected] for eligibility).
VR training is increasingly affordable due to declining hardware costs (e.g., VR headsets like Oculus Quest start at $300) and cloud-based platforms that reduce infrastructure needs. Institutions like MPT and MITAGS offer blended programs combining online theory with VR practicals, enhancing accessibility for remote learners.
Latest Trends and Future Outlook
VR maritime training is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and industry demand for efficient, scalable solutions. Key trends include:
- Haptic Feedback Gloves: Enable tactile sensations, such as feeling resistance when operating valves or equipment.
- Multiplayer VR Drills: Facilitate group coordination and leadership training in simulated emergencies.
- AI-Driven Assessments: Evaluate accuracy, timing, and communication for precise STCW certification.
- Cloud-Based VR Centers: Provide global access to STCW courses, ideal for remote regions.
- Metaverse Integration: Combines VR with virtual campuses for networking, career guidance, and immersive learning.
Industry Partnerships
Companies like KVH Videotel and OMS-VR are collaborating to expand VR training portfolios. Their agreement aims to develop over 40 new VR training segments, covering STCW-critical safety, cargo, and engineering tasks. Kongsberg Digital’s K-Sim VR and Seably’s immersive modules are already approved by global maritime academies Ascending…
System: …ending maritime academies, showcasing the growing adoption of these technologies.
Forecast
By 2030, over 60% of STCW training is expected to incorporate VR or mixed reality components, driven by cost savings, scalability, and enhanced learning outcomes. The integration of VR with cloud-based platforms and AI analytics will further democratize access to high-quality training, particularly for seafarers in developing regions.
FAQs: People Also Ask
Is VR Training Approved Under STCW?
Yes, VR training is approved for STCW competencies when delivered by certified institutions and aligned with IMO model courses. It is valid for both initial certifications and refreshers.
How Are Trainees Assessed in VR Environments?
Assessments track:
- Decision-making accuracy
- Response time
- Correct sequence of actions
- Communication effectiveness
AI-driven analytics or instructor-led evaluations ensure compliance with STCW standards.
Can VR Replace Physical Simulators Entirely?
VR complements physical simulators for many modules but cannot fully replace advanced bridge or engine simulators for certifications like Officer of the Watch (OOW) or Certificate of Competency (COC). It excels in basic safety and scenario-based training.
Is VR Training Affordable for Maritime Schools?
Yes, with VR headsets costing as little as $300 and cloud-based platforms reducing infrastructure needs, VR training is increasingly cost-effective and scalable.
Conclusion: A Safer Sea Through Immersive Learning
STCW-compliant VR maritime training is redefining seafarer education by combining immersive technology with rigorous regulatory standards. It offers a safe, cost-effective, and engaging way to prepare mariners for real-world challenges, from firefighting to crisis management. As the maritime industry embraces digital transformation, VR training is becoming the new standard for safety, efficiency, and competency.
Call to Action: Maritime students, instructors, and training providers should explore STCW-certified VR platforms to enhance learning and ensure safer seas. Contact institutions like MITAGS or MPT to integrate VR into your training journey.
Happy Boating!
Share STCW-Compliant VR Maritime Training with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read VR & Simulation-Based Learning for Engine Room Officers until we meet in the next article.






