Marine Tank Monitors and Boat Tank Sensors Guide
Discover the ultimate guide to marine tank monitors and boat tank sensors. Learn types, features, installation, and maintenance for precise water level monitoring.
Marine tank monitors and boat tank sensors are essential tools for boat owners, ensuring precise monitoring of water, fuel, and wastewater levels. These devices prevent overflows, detect leaks, and optimize resource management, saving time and money. This comprehensive guide explores sensor types, key selection factors, installation, maintenance, and smart integration options to help you choose the best system for your vessel.
Why Marine Tank Sensors Matter
Managing tank levels on a boat is critical for safety, efficiency, and convenience. Running out of fresh water or overfilling a holding tank can disrupt your journey and lead to costly repairs. Marine tank sensors provide real-time data, allowing you to monitor levels accurately and make informed decisions. They also reduce the need for manual checks, which are time-consuming and prone to error.
For example, a 40-foot yacht with multiple tanks (fresh water, gray water, black water, and fuel) benefits immensely from automated monitoring. Sensors can alert you to low fresh water levels or a full holding tank, preventing unexpected trips to marinas or environmental mishaps.
Types of Marine Tank Level Sensors
Marine tank sensors fall into three main categories: contact, non-contact, and external. Each type uses different technology to measure liquid levels, offering unique advantages based on your tank’s characteristics and operational needs.
1. Contact Sensors
Contact sensors physically interact with the liquid, making them robust and reliable for marine environments.
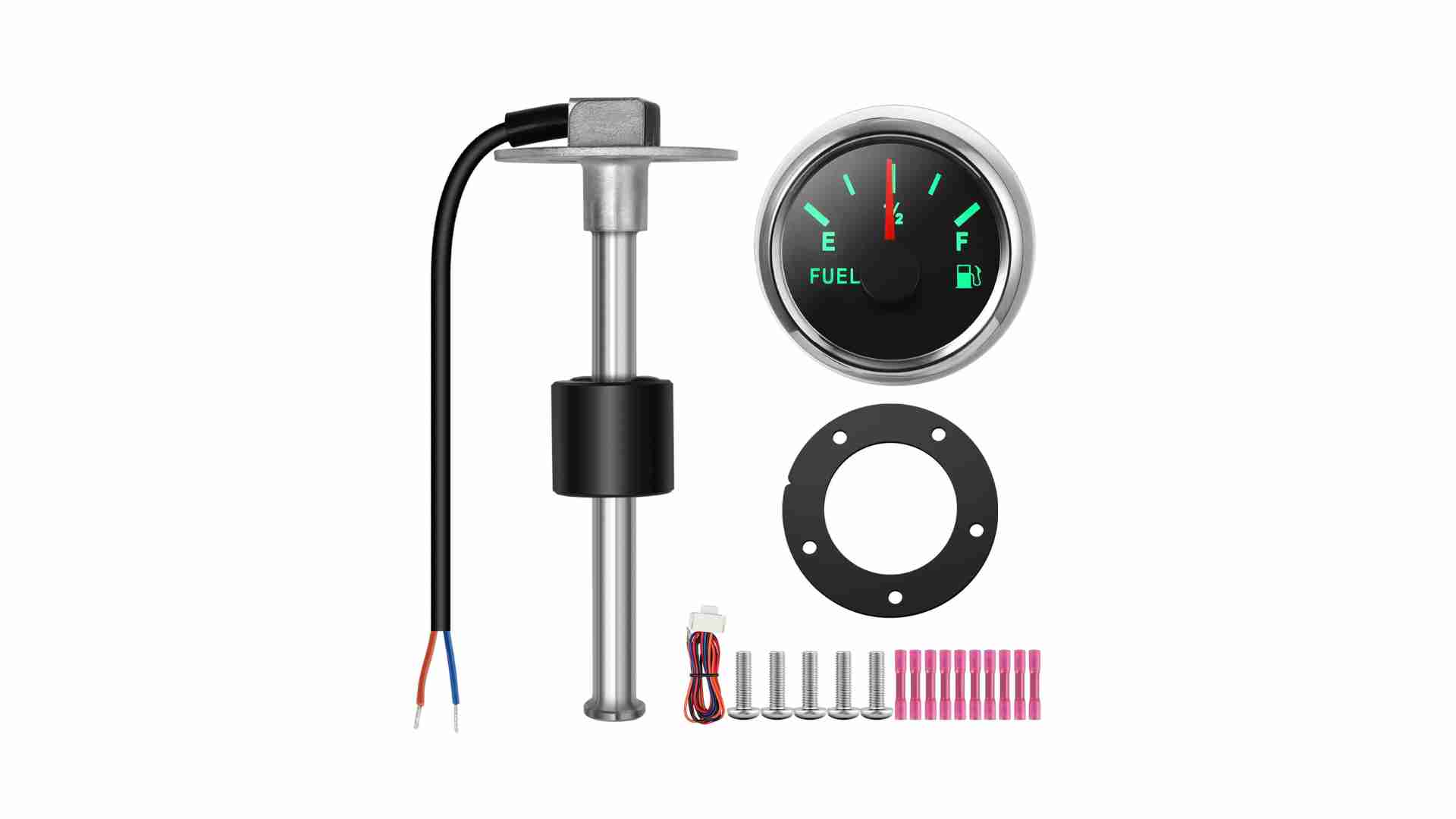
- Submersible Pressure Sensors: These sensors are installed at the tank’s bottom and measure hydrostatic pressure caused by the liquid’s weight. The pressure is converted into an electrical signal, providing accurate level readings. They are ideal for deep tanks and harsh conditions, such as black water tanks, due to their durability. Price Range: $100–$300.
- Float Sensors: A float moves up or down with the liquid level, triggering a switch or sending a signal. They are cost-effective and simple, suitable for smaller tanks or budget-conscious setups. However, they may be less accurate in turbulent conditions. Price Range: $50–$150.
- Capacitance Sensors: These use a probe submerged in the liquid, detecting changes in capacitance as the liquid level varies. They are versatile for fresh and wastewater tanks but require regular cleaning to maintain accuracy. Price Range: $150–$400.
2. Non-Contact Sensors
Non-contact sensors measure levels without touching the liquid, making them low-maintenance and suitable for irregular tanks.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These emit sound waves that reflect off the liquid surface, calculating the distance to determine the level. They work well with various tank materials and shapes, offering high accuracy. However, they can be affected by foam or vapor. Price Range: $200–$500.
- Radar Sensors: Using radar waves, these sensors provide precise measurements even in harsh conditions like high humidity or temperature fluctuations. They are expensive but ideal for critical applications. Price Range: $500–$1,200.
3. External Sensors
External sensors measure levels from outside the tank, minimizing installation complexity.
- Capacitance Charge Probes: Mounted externally, these detect capacitance changes through the tank wall. They are non-invasive but may require calibration for accuracy. Price Range: $100–$250.
- Optical Sensors: These use infrared light to detect liquid presence externally. They are niche and less common but useful for specific applications. Price Range: $150–$350.
Comparison Table: Marine Tank Sensor Types
| Sensor Type | Accuracy | Durability | Maintenance | Price Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pressure | High | High | Moderate | $100–$300 | Deep, harsh tanks |
| Float | Moderate | Moderate | Low | $50–$150 | Budget, small tanks |
| Capacitance | High | Moderate | High | $150–$400 | Fresh/wastewater tanks |
| Ultrasonic | High | High | Low | $200–$500 | Irregular tanks |
| Radar | Very High | High | Low | $500–$1,200 | Critical, harsh environments |
| External Capacitance | Moderate | High | Low | $100–$250 | Non-invasive setups |
| Optical | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | $150–$350 | Specialized applications |
Key Factors for Choosing a Marine Tank Sensor
Selecting the right sensor depends on your boat’s specific needs. Here are the critical factors to consider:
1. Tank Type and Shape
- Shape: Irregular or narrow tanks favor non-contact sensors like ultrasonic or radar, which don’t require internal components. Rectangular tanks suit float or submersible sensors.
- Material: Stainless steel or plastic tanks may influence sensor compatibility. For example, external capacitance sensors work better with non-metallic tanks.
- Contents: Fresh water, gray water, black water, or fuel require sensors designed for their specific properties. Black water tanks need corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel.
2. Fluid Type
- Sensors for fresh water are simpler, while those for wastewater or fuel must handle corrosive or viscous fluids. Capacitance sensors excel in wastewater, while radar sensors are ideal for fuel tanks.
3. Accuracy and Precision
- High-accuracy sensors (e.g., radar, submersible) are crucial for large tanks or critical systems. For smaller tanks, moderate accuracy (e.g., float sensors) may suffice.
- Calibration points enhance precision. Regular tanks need at least two points, while irregular tanks benefit from three or more (up to 11 for complex systems).
4. Environmental Conditions
- Marine environments expose sensors to vibration, humidity, and temperature extremes. Choose sensors with IP67 or higher ratings for water resistance and stainless steel construction for corrosion resistance.
- Example: Radar sensors perform well in humid conditions, while float sensors may fail in high-vibration scenarios.
5. Power and Output
- Most sensors operate on 12V DC, standard for boats. Ensure compatibility with your power system.
- Output types include analog (0–5V, 4–20mA) for precision or digital for easy integration with control panels. Resistance sensors (0–65 kΩ) and voltage sensors (0–75V) are widely supported.
6. Accessibility and Installation
- External sensors are easier to install and maintain, ideal for retrofitting. Submersible sensors require tank access but offer high accuracy.
- Consider maintenance needs: Capacitance sensors need frequent cleaning, while ultrasonic sensors are low-maintenance.
7. Brand Reliability
- Trusted brands like Faria, VDO, Raymarine, Simrad, and Garmin offer durable, high-performance sensors. Emerging brands like Waltero provide smart, integrated solutions.
- Check warranty and support options, as marine environments demand robust after-sales service.
Installation Guide for Marine Tank Sensors
Proper installation ensures accurate readings and long sensor life. The process varies by sensor type, but general steps apply:
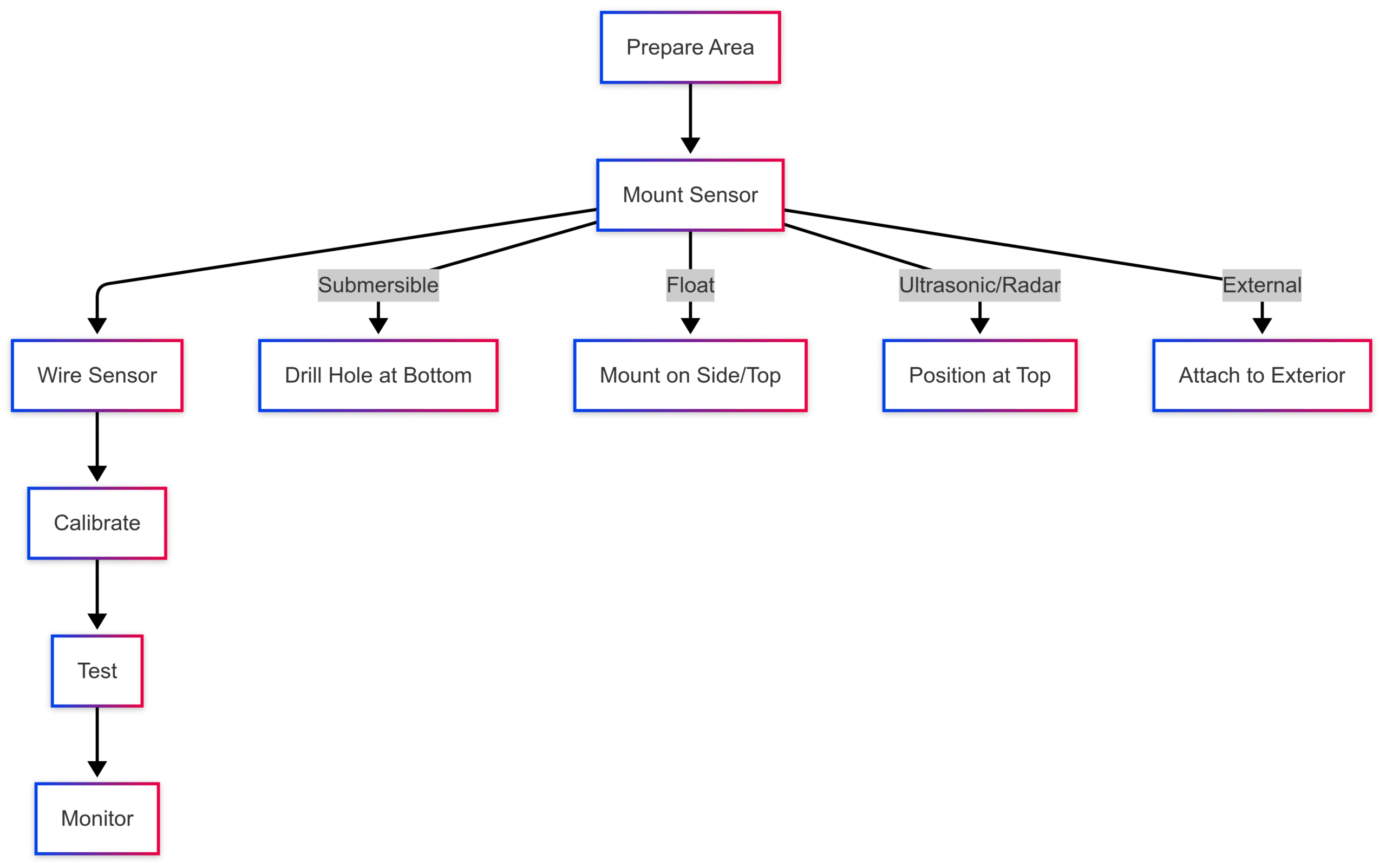
- Prepare the Area: Ensure the tank is accessible, clean, and drained if necessary. Gather tools (screwdrivers, marine-grade connectors, sealant) and read the manufacturer’s manual.
- Mount the Sensor:
- Submersible: Install at the tank’s bottom via a drilled hole, sealing with marine-grade sealant.
- Float: Mount on the side or top, ensuring the float moves freely.
- Ultrasonic/Radar: Position at the tank’s top, avoiding obstructions.
- External: Attach to the tank’s exterior, ensuring firm contact.
- Wire the Sensor: Connect to a control panel or gauge using marine-grade wiring. Use corrosion-resistant connectors and secure cables to prevent vibration damage.
- Calibrate:
- For regular tanks, set at least two calibration points (empty and full).
- For irregular tanks, use 3–11 points for precision.
- Example: For a 100-liter fuel tank, fill it, note the sensor reading (e.g., 5V), then drain and record the empty reading (e.g., 0V). Input these into the control panel.
- Test: Fill the tank partially and verify readings on the control panel. Adjust calibration if needed.
- Monitor: Check readings regularly during initial use to ensure accuracy.
Chart: Installation Workflow
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance extends sensor life and ensures accuracy. Follow these guidelines:
Maintenance Tips
- Inspect Monthly: Check for corrosion, wear, or debris. Clean sensors like capacitance probes to prevent buildup.
- Calibrate Annually: Recalibrate sensors to account for tank changes or sensor drift.
- Replace as Needed: Sensors typically last 4–5 years (2–3 in harsh conditions). Replace if readings are erratic or the sensor is damaged.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- False Readings: Check for obstructions, clean the sensor, or recalibrate. For hydrostatic sensors, ensure no condensation buildup.
- Signal Interference: Verify wiring integrity and ground connections.
- Erratic Readings: Reorient the sensor or replace it if faulty. For RV-style sensors, pouring boiling water down drains may reset readings.
Maintenance Schedule Table
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect for Damage | Monthly | Check corrosion, debris |
| Clean Sensor | Every 3 Months | Especially for capacitance |
| Recalibrate | Annually | Adjust for tank changes |
| Replace Sensor | 4–5 Years | Sooner in harsh conditions |
Smart Integration with Waltero
Modern marine tank monitoring systems are embracing smart technology, and Waltero leads with innovative solutions. Their end-to-end platform includes sensors, communication, controllers, communication modules, and cloud-based data management, offering seamless integration for efficient water management.
Waltero W-Sensor
The W-Sensor attaches to existing analog meters, transforming them into digital smart meters. It supports LTE, LoRa, and WiFi for real-time data transmission, enhancing monitoring capabilities.
- Benefits:
- Extends the life of analog meters.
- Provides precise readings for remote monitoring.
- Simplifies data management for multiple tanks.
- Applications: Ideal for retrofitting older boats or managing complex tank systems on large vessels.
Custom Solutions
Waltero offers modular sensors tailored for marine applications, such as monitoring reservoirs, fuel tanks, or early warning systems for coastal hazards. These sensors are durable, easy to install, corrosion-resistant, and come with flexible calibration ranges.
Comparing Top Brands and Value
Choosing a brand involves balancing features, durability, and cost. Below is a comparison of leading marine sensor brands:
| Brand | Key Features | Price Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raymarine | Wireless, high-accuracy, smart integration | $300–$1,500 | Premium yachts |
| Garmin | Robust, multi-tank support | $250–$800 | Mid-to-high-end boats |
| Faria | Affordable, reliable | $100–$400 | Budget-conscious setups |
| VDO | Durable, precise | $150–$500 | Commercial vessels |
| Waltero | Smart, customizable, retrofit | $200–$600 | Smart tech, retrofitting |
Value Analysis
- Budget: Faria and VDO offer cost-effective solutions for smaller boats.
- Mid-Range: Garmin and Waltero provide durability and smart features for mid-sized vessels.
- Premium: Raymarine excels in high-accuracy, wireless systems for luxury yachts.
FAQs
What’s the difference between a level switch and a level sensor?
How often should I check my tank levels?
How do I maintain my sensor?
Can I retrofit my existing system?
What’s the best sensor for irregular tanks?
Conclusion
Marine tank monitors and boat tank sensors are indispensable for efficient, safe boating. By understanding sensor types, key selection factors, and proper installation, you can ensure accurate monitoring of your vessel’s tanks. Regular maintenance and smart integrations like Waltero’s solutions elevate performance, while choosing reliable brands guarantees longevity. Invest in the right sensor today to optimize your water and fuel management, ensuring smooth sailing every time.
Happy Boating!
Share Marine Tank Monitors and Boat Tank Sensors Guide with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read What should I subscribe to (Marine traffic or vessels finder) until we meet in the next article.






