MAN B&W Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Diesel Engines
Discover MAN B&W two-stroke slow-speed diesel engines: fuel-flexible, high-efficiency propulsion for ships, meeting modern maritime demands.
In the maritime industry, propulsion systems are the heartbeat of global shipping, driving massive vessels across oceans to transport goods and resources. Among the leading solutions in this domain are MAN B&W two-stroke slow-speed diesel engines, renowned for their reliability, efficiency, and adaptability. Manufactured by MAN Energy Solutions, these engines power a significant portion of the world’s merchant fleet, including container ships, bulk carriers, and tankers. Their ability to operate on a range of fuels, from traditional heavy fuel oil to sustainable alternatives like methanol and LNG, positions them as a cornerstone of modern and future-ready maritime propulsion.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of MAN B&W two-stroke slow-speed diesel engines, detailing their design, operational principles, technological advancements, and environmental considerations. With a focus on their key features, engine types, and real-world applications, we aim to offer a comprehensive resource for understanding these engineering marvels and their role in shaping the future of shipping.
Evolution of MAN B&W Two-Stroke Engines
The legacy of MAN B&W two-stroke engines traces back to the early 20th century, rooted in the pioneering work of Burmeister & Wain (B&W), a Danish shipyard with a rich history in marine engineering. In 1980, MAN Diesel acquired B&W, merging their expertise to advance diesel engine technology. This collaboration laid the foundation for the development of robust, high-performance two-stroke engines tailored for large-scale maritime applications.
The 1990s marked a significant milestone with the introduction of the MC series, which set new benchmarks for fuel efficiency and performance. These engines incorporated advanced turbocharging and optimized combustion processes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining high power output. By the early 2000s, the MC series had captured over 70% of the market share for large marine diesel engines, reflecting their reliability and industry trust.
The launch of the ME-C series in the early 2000s further revolutionized the field. By integrating electronic control systems, MAN B&W enhanced precision in fuel injection and combustion management, improving efficiency and enabling compatibility with alternative fuels like LNG and methanol. Today, the portfolio includes specialized variants such as ME-GI, ME-LGIM, and ME-LGIP, each designed to meet specific fuel and operational requirements, ensuring flexibility in a rapidly evolving industry.
Key Design Features
MAN B&W two-stroke engines are engineered with precision, incorporating components that ensure durability, efficiency, and high performance. Below are the primary design elements:
- Cylinder Block: The cylinder block is the structural backbone, housing multiple cylinders where combustion occurs. Its robust design withstands high pressures and temperatures, ensuring longevity in demanding marine environments.
- Piston and Connecting Rod: Pistons endure extreme combustion pressures, converting thermal energy into mechanical motion. Connected to the crankshaft via rods, they drive the ship’s propeller with precision.
- Turbocharger: By harnessing exhaust gases to compress incoming air, turbochargers increase air density, enhancing combustion efficiency and power output.
- Fuel Injection System: Advanced direct injection systems deliver precise fuel quantities, optimizing combustion and reducing emissions.
- Scavenging Ports: These ports enable efficient air intake and exhaust expulsion, ensuring clean combustion cycles and maintaining engine performance.
- Lubrication System: A sophisticated lubrication system minimizes friction, reducing wear and extending engine lifespan.
- Crosshead Design: The crosshead separates the piston from the connecting rod, reducing side thrust and enhancing durability in slow-speed operations.
- Electro-Hydraulic Control: In ME series engines, electronic actuators replace traditional mechanical components like camshafts, offering precise control over fuel injection and valve timing.
These components work in harmony to deliver high power density, operational stability, and fuel efficiency, making MAN B&W engines ideal for large vessels.
Operational Principles of Two-Stroke Engines
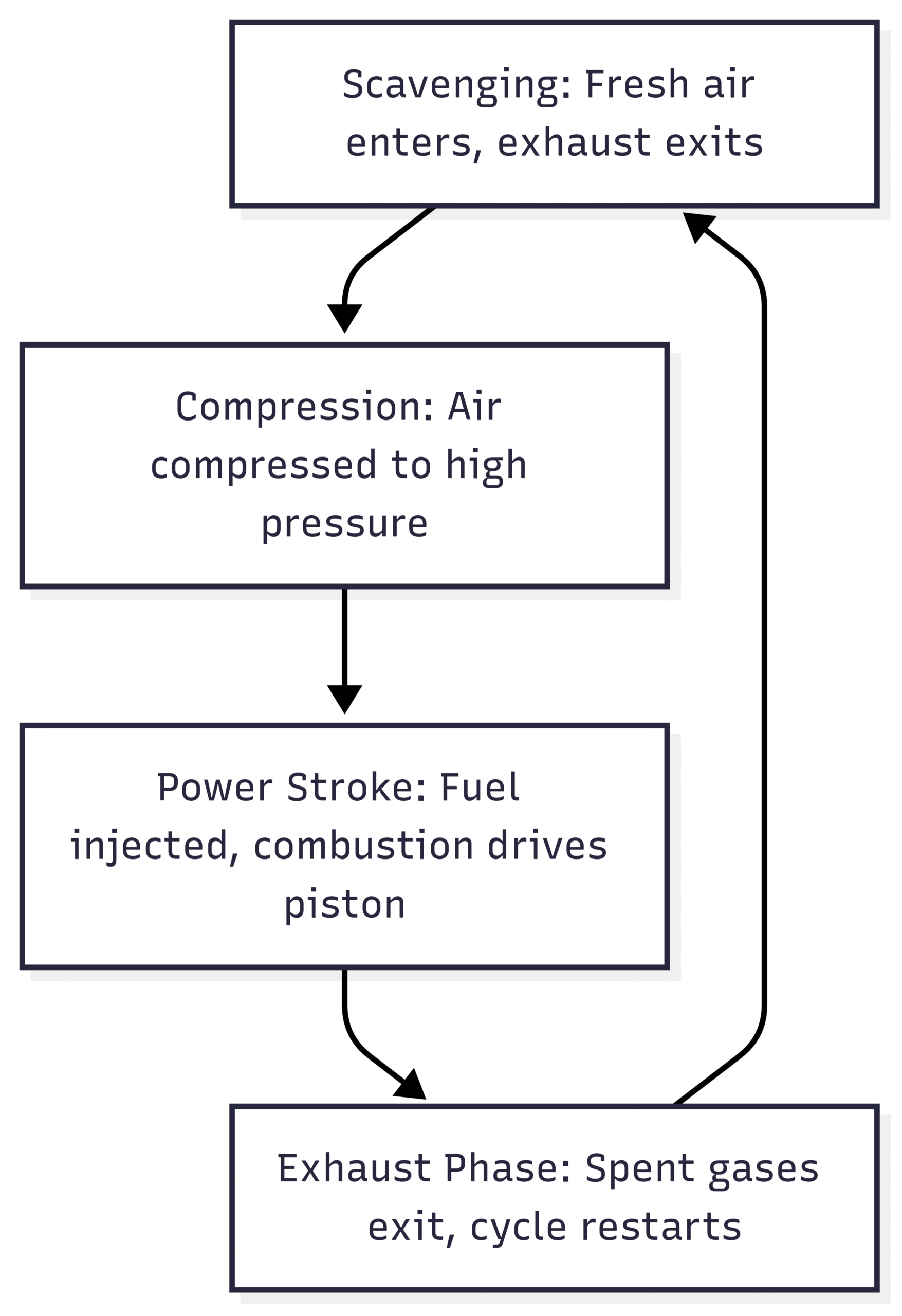
The two-stroke cycle is a hallmark of MAN B&W engines, offering simplicity and high power output compared to four-stroke designs. Unlike four-stroke engines, which complete a cycle in two crankshaft revolutions, two-stroke engines complete a cycle in one, doubling the power strokes per revolution. This efficiency is critical for marine applications where low-speed, high-torque propulsion is essential. The operational cycle consists of four key phases:
- Scavenging: As the piston descends after combustion, it uncovers scavenging ports, allowing fresh air to enter and push out exhaust gases. Turbochargers enhance this process by supplying compressed air, improving combustion efficiency.
- Compression: The piston ascends, compressing air to high pressures (up to 30 bar) and temperatures (around 600°C). This prepares the cylinder for ignition without spark plugs, a hallmark of diesel engines.
- Power Stroke: Near top dead center, fuel is injected into the compressed air, igniting instantly. The resulting combustion drives the piston downward, generating mechanical energy to power the propeller.
- Exhaust Phase: As the piston descends again, exhaust ports open, expelling spent gases while fresh air enters, restarting the cycle.
This cycle, illustrated below in a chart, ensures high torque at low speeds, ideal for large ships.
Engine Portfolio and Specifications
MAN B&W offers a diverse range of two-stroke engines, each tailored to specific vessel types and fuel requirements. Below is an overview of the key models, their specifications, and applications.
MAN B&W ME-C
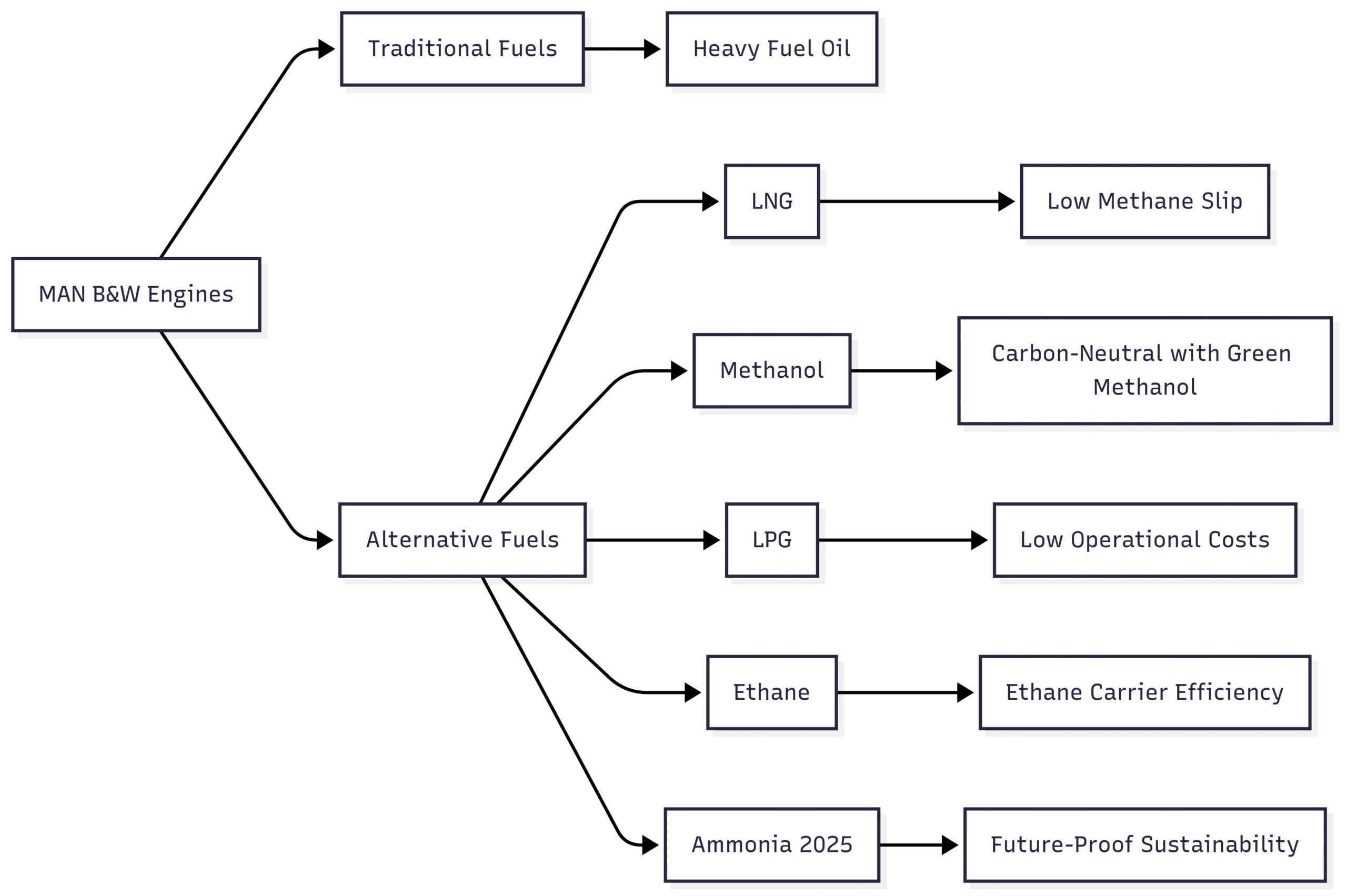
- Description: Electronically controlled, offering superior performance, compactness, and fuel flexibility.
- Fuel Options: Heavy fuel oil, LNG, methanol, LPG, ethane, and ammonia (from 2025).
- Engine Speed: 56–167 rpm.
- Power Output: 4,350–82,440 kW at L1.
- Applications: Container ships, bulk carriers, tankers.
- Advantages: High fuel injection pressure, precise rate shaping, retrofit capability for alternative fuels.
MAN B&W ME-GI
- Description: Dual-fuel engine optimized for LNG, with low methane slip and high efficiency.
- Fuel Options: LNG, bio-methane, SNG, fuel oil.
- Engine Speed: 56–167 rpm.
- Power Output: 4,350–82,440 kW at L1.
- Applications: LNG carriers, large commercial vessels.
- Advantages: Environmentally friendly, high fuel efficiency, operational flexibility.
MAN B&W ME-GIE
- Description: Designed for ethane carriers, based on ME-GI technology.
- Fuel Options: Ethane, fuel oil.
- Engine Speed: 72–100 rpm.
- Power Output: 8,600–21,440 kW at L1.
- Applications: Ethane carriers.
- Advantages: Competitive fuel consumption, operational stability.
MAN B&W ME-LGIM
- Description: Dual-fuel engine optimized for methanol, offering carbon-neutral propulsion with green methanol.
- Fuel Options: Methanol, fuel oil.
- Engine Speed: 56–125 rpm.
- Power Output: 6,950–82,440 kW at L1.
- Applications: Vessels aiming for low-emission propulsion.
- Advantages: Over 600,000 hours of methanol operation, reduced sulfur and particulate emissions.
MAN B&W ME-LGIP
- Description: The only two-stroke engine designed for LPG propulsion.
- Fuel Options: LPG, fuel oil.
- Engine Speed: 72–103 rpm.
- Power Output: 8,600–22,720 kW at L1.
- Applications: LPG carriers.
- Advantages: Low operational costs, simple retrofit solution.
| Engine Model | Fuel Options | Engine Speed (rpm) | Power Output (kW) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME-C | Fuel oil, LNG, methanol, LPG, ethane, ammonia | 56–167 | 4,350–82,440 | Container ships, bulk carriers, tankers |
| ME-GI | LNG, bio-methane, SNG, fuel oil | 56–167 | 4,350–82,440 | LNG carriers, commercial vessels |
| ME-GIE | Ethane, fuel oil | 72–100 | 8,600–21,440 | Ethane carriers |
| ME-LGIM | Methanol, fuel oil | 56–125 | 6,950–82,440 | Low-emission vessels |
| ME-LGIP | LPG, fuel oil | 72–103 | 8,600–22,720 | LPG carriers |
Technological Advancements
MAN B&W two-stroke engines have evolved to meet modern demands for efficiency, sustainability, and compliance with international regulations. Key advancements include:
- Dual-Fuel Capabilities: The ME-C series and its variants can operate on alternative fuels like LNG, methanol, and LPG, with ammonia compatibility planned for 2025. This flexibility aligns with IMO Tier III emission standards, enabling operators to adapt to stricter regulations and fluctuating fuel markets.
- Electronic Control Systems: The ME series uses electro-hydraulic controls to optimize fuel injection and valve timing, improving efficiency across varying loads. This reduces fuel consumption (typically 170–175 g/kWh at optimal loads) and emissions.
- Modular Design: The modular architecture simplifies maintenance and retrofitting, minimizing downtime and costs. Components like fuel injectors and turbochargers can be upgraded without major overhauls.
- Emissions Reduction: Technologies like exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) reduce NOx and SOx emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Environmental Sustainability
As the maritime industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, MAN B&W engines are at the forefront of sustainable propulsion. The ME-LGIM, for instance, achieves carbon-neutral operation when using green methanol, significantly reducing sulfur and particulate emissions. The ME-GI’s low methane slip makes it one of the most environmentally friendly LNG-fueled engines available. These advancements align with the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 50% by 2050 compared to 2008 levels.
The following chart illustrates the fuel flexibility of MAN B&W engines and their environmental impact:
Real-World Applications
MAN B&W two-stroke engines power a wide range of vessels, demonstrating their versatility and reliability:
- Container Ships: Maersk’s fleet, for example, uses the 12K98MC engine, delivering over 75,000 kW for high-speed transoceanic voyages. These engines balance speed and fuel efficiency, critical for global trade.
- Bulk Carriers: The 6S50MC engine provides high torque at low RPMs, ideal for transporting heavy cargo like coal or grain over long distances.
- Tankers: Engines like the ME-C series offer low specific fuel consumption (around 171 g/kWh), ensuring cost-effective operation for oil and chemical tankers.
- LNG and LPG Carriers: The ME-GI and ME-LGIP engines are tailored for gas carriers, offering high efficiency and compliance with emission standards.
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
To maximize performance and longevity, MAN B&W engines require diligent maintenance:
- Routine Inspections: Regular checks of lubricating oil, coolant, and fuel systems prevent wear and ensure optimal performance.
- Turbocharger Maintenance: Cleaning and inspecting turbochargers maintain efficient air intake and combustion.
- Fuel System Checks: High-quality fuel and regular injector maintenance prevent performance degradation.
- Exhaust System Care: Clearing blockages and implementing EGR systems ensure compliance with emission standards.
Pricing and Cost Considerations
While exact pricing varies based on engine model, customization, and market conditions, MAN B&W two-stroke engines are a significant investment. Approximate costs for new installations range from $5 million to $20 million, depending on power output and fuel configuration. Retrofitting for alternative fuels, such as converting an ME-C to ME-LGIM, can cost $1–3 million per engine. For precise pricing, contact MAN Energy Solutions via their official website.
Future Outlook
As the maritime industry navigates stricter environmental regulations and the shift toward decarbonization, MAN B&W two-stroke engines are well-positioned to lead. Their fuel flexibility, particularly with ammonia compatibility on the horizon, ensures adaptability to future fuel trends. Ongoing innovations in electronic controls and emissions reduction technologies will further enhance their efficiency and sustainability, solidifying their role in powering the global fleet.
Conclusion
MAN B&W two-stroke slow-speed diesel engines represent the pinnacle of maritime propulsion, combining high power, efficiency, and fuel flexibility. From their robust design to their advanced electronic controls and dual-fuel capabilities, these engines meet the demands of modern shipping while addressing environmental challenges. With a proven track record in container ships, bulk carriers, and gas carriers, they remain a trusted choice for shipowners worldwide. As the industry evolves, MAN B&W’s commitment to innovation ensures these engines will continue to drive the future of sustainable maritime transport.
Happy Boating!
Share MAN B&W Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Diesel Engines with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read Water Mist Fire Fighting Systems in Ship Engine Rooms until we meet in the next article.