Explore technological advancements in shipping: automation, AI, green tech, and more drive efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
The shipping industry, a backbone of global trade, transports over 80% of the world’s goods by volume. As global commerce grows, the sector faces increasing demands for efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Technological advancements are transforming maritime operations, from automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to sustainable practices and digitalization. These innovations streamline processes, reduce environmental impact, and enhance safety, positioning the industry for a resilient future. This article explores the key technological advancements revolutionizing the shipping sector, their benefits, challenges, and future potential.
1. Automation and Robotics in Shipping
Automation is reshaping maritime operations, particularly in ports and on vessels. By reducing human intervention, automation enhances efficiency, cuts costs, and improves safety.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are driverless vehicles used in ports to transport containers between ships, storage areas, and trucks. These vehicles operate using sensors, GPS, and advanced software, navigating complex port environments with precision. AGVs reduce congestion, speed up container handling, and minimize human error. Major ports like Rotterdam and Singapore have adopted AGVs, reporting up to 30% faster container turnaround times.
Automated Cranes
Robotic cranes, equipped with AI and sensors, automate the loading and unloading of cargo. These cranes operate with high precision, reducing the risk of accidents and increasing throughput. For example, the Port of Los Angeles uses automated cranes to handle over 7 million containers annually, cutting loading times by 20%. The table below compares manual and automated crane performance:
| Metric | Manual Cranes | Automated Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Containers per Hour | 20-25 | 30-40 |
| Error Rate | 2-3% | <1% |
| Operational Cost | High (Labor) | Lower (Long-term) |
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates repetitive administrative tasks such as data entry, invoicing, and document processing. By integrating RPA, shipping companies reduce operational costs and free up staff for strategic roles. For instance, Maersk implemented RPA to automate 15% of its back-office tasks, saving millions annually.
Autonomous Ships
Autonomous ships, equipped with AI, sensors, and navigation systems, are a frontier in maritime innovation. These vessels can operate with minimal or no human intervention, reducing crew costs and human error. Companies like Rolls-Royce and Kongsberg are developing autonomous ships, with prototypes like the Yara Birkeland, a fully electric and autonomous container ship, already operational in Norway. Autonomous ships promise up to 15% fuel savings and enhanced safety by avoiding human-related navigational errors.
Chart: Autonomous Ship Workflow
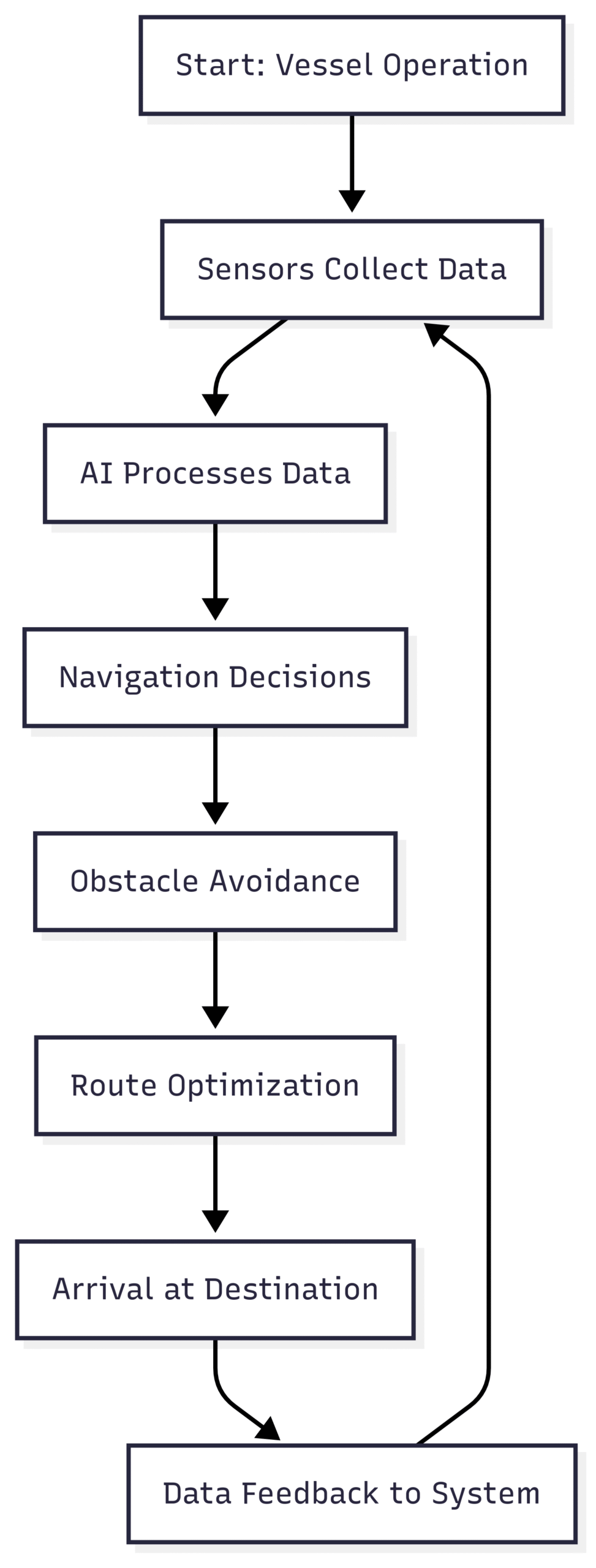
2. Data Analytics and Digitalization
Digital technologies are revolutionizing how shipping companies manage operations, optimize routes, and enhance transparency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices, such as sensors on containers and vessels, provide real-time data on location, temperature, and equipment health. This enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by up to 25%. For example, IoT systems on Maersk vessels monitor engine performance, cutting maintenance costs by 10%. IoT also supports route optimization, saving fuel and reducing emissions.
Cloud Computing
Cloud-based platforms enable seamless data storage and sharing among stakeholders, including shippers, port authorities, and logistics providers. These platforms improve collaboration and scalability. For instance, the TradeLens platform, powered by IBM’s cloud, connects over 300 organizations, streamlining global trade documentation.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain provides a secure, transparent ledger for tracking shipments and transactions. It reduces fraud, enhances supply chain visibility, and automates processes through smart contracts. The Global Shipping Business Network (GSBN) uses blockchain to process over 1 million digital documents annually, cutting processing times by 50%. The diagram below illustrates blockchain’s role in shipping:
Chart: Blockchain in Shipping
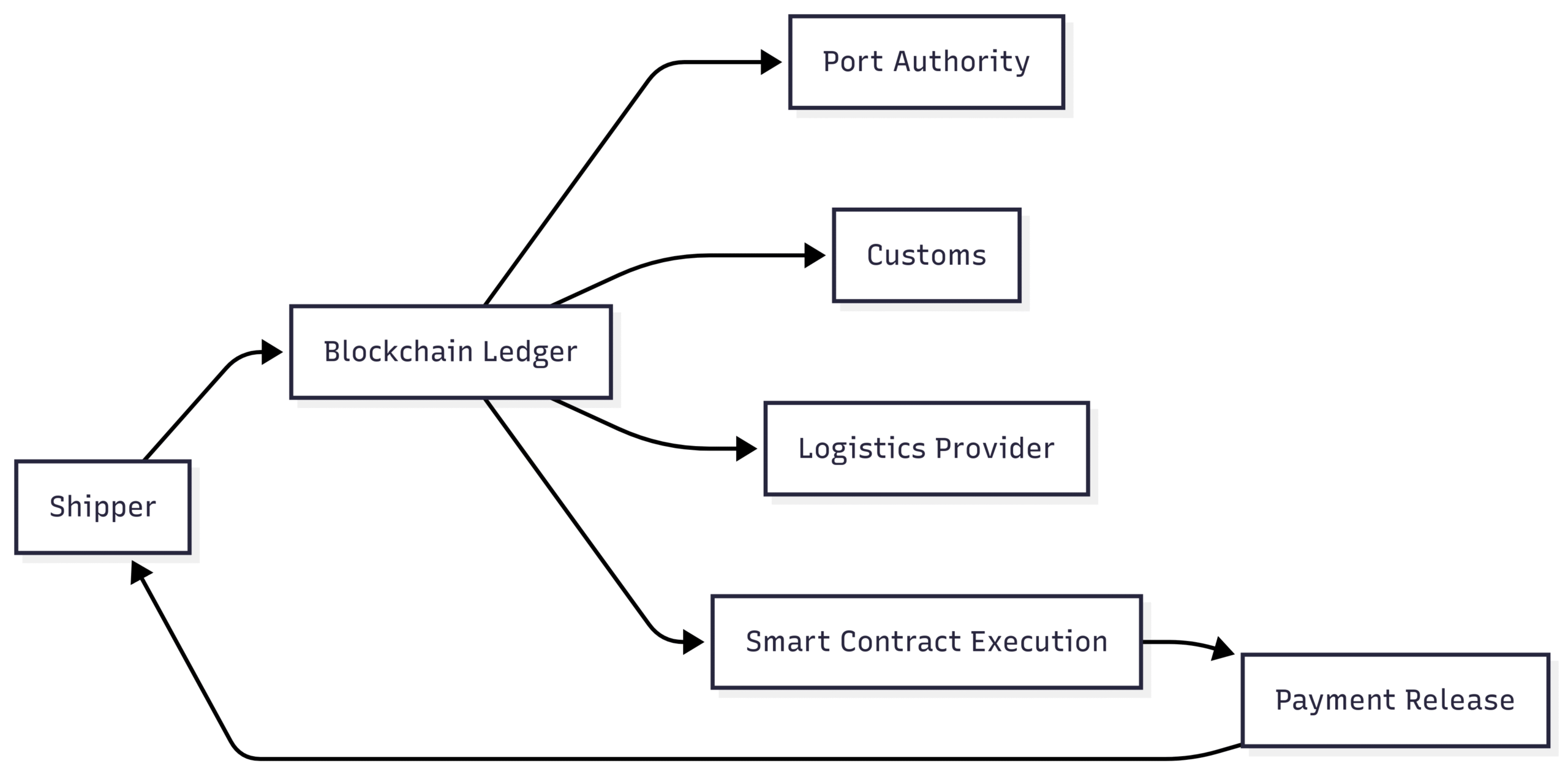
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, such as ships or ports, used for simulations and predictive analytics. They help optimize operations and test scenarios without real-world risks. For example, the Port of Singapore uses digital twins to simulate container flows, improving efficiency by 15%.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning enhance route optimization, demand forecasting, and risk assessment. AI-driven platforms like Sinay’s calculate estimated times of arrival (ETAs) with 95% accuracy, improving scheduling. Machine learning models analyze historical data to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime by 20%.
3. Sustainable Shipping Practices
Sustainability is a priority as the shipping industry accounts for 3% of global CO2 emissions. Technological advancements are driving greener practices.
Alternative Fuels
The industry is shifting to low-carbon fuels like liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen. LNG reduces emissions by 25% compared to traditional fuels, while ammonia and hydrogen offer near-zero emissions. Companies like CMA CGM are investing $1.5 billion in LNG-powered vessels, with 20 ships already in operation.
Wind-Assisted Propulsion
Wind-assisted technologies, such as rotor sails and kites, reduce fuel consumption by 5-20%. Norsepower’s rotor sails, installed on vessels like the Maersk Pelican, cut fuel use by 8% on average.
Hull Optimization
Advanced hull designs and anti-fouling coatings reduce drag, improving fuel efficiency by up to 10%. For example, Nippon Paint’s low-friction coatings are used on over 5,000 vessels globally.
Green Ship Recycling
Sustainable recycling methods, such as closed-loop dismantling, minimize environmental impact. The EU’s Ship Recycling Regulation enforces eco-friendly practices, with compliant yards in Turkey and India processing over 70% of global ship recycling.
Table: Comparison of Alternative Fuels
| Fuel Type | Emission Reduction | Cost per Ton | Adoption Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| LNG | 25% | $600-$800 | High |
| Methanol | 15-20% | $400-$600 | Moderate |
| Ammonia | Near-zero | $700-$900 | Low |
| Hydrogen | Near-zero | $1,000-$1,500 | Emerging |
4. Port Technology
Ports are critical nodes in global trade, and technological advancements are enhancing their efficiency.
Port Automation
Automated terminals, equipped with AGVs, cranes, and robotic stackers, reduce turnaround times and labor costs. The Port of Rotterdam’s automated terminal handles 3.5 million containers annually, with 30% lower operational costs than traditional terminals.
Digitalization
Digital platforms streamline port operations, from container tracking to cargo planning. The Port of Singapore’s digital system, SYNC, reduces vessel waiting times by 25% through real-time data sharing.
5. Cybersecurity in Shipping
As digitalization increases, so does the risk of cyber threats. The NotPetya attack in 2017 cost Maersk $300 million, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity. Measures include:
- Firewalls and Encryption: Protect data transmission.
- AI-based Threat Detection: Identifies anomalies in real-time.
- Crew Training: Educates staff on phishing and malware risks.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) mandates cybersecurity protocols under the 2021 Cyber Risk Management guidelines, ensuring vessels and ports are secure.
6. Emerging Technologies
Drones
Drones are used for remote inspections and spare part deliveries. The Port of Singapore employs drones to deliver parts to vessels, reducing delivery times by 70%. Drones also inspect hard-to-reach areas, improving safety.
3D Printing
3D printing enables on-demand production of spare parts onboard, reducing downtime and logistics costs. Wilhelmsen’s 3D printing service produces parts for 10% of traditional costs.
Advanced Monitoring Systems
These systems use sensors and satellite imagery to monitor environmental conditions, such as water quality and vessel traffic. They help prevent pollution and optimize navigation, reducing fuel use by 5%.
New Trade Routes
Climate change has opened Arctic routes, reducing shipping times between Asia and Europe by 10-15 days. However, these routes require advanced navigation systems to ensure safety.
Benefits of Technological Advancements
- Efficiency: Automation and digitalization cut turnaround times by 20-30%.
- Cost Savings: AGVs and RPA reduce labor costs by up to 25%.
- Sustainability: Alternative fuels and hull optimization lower emissions by 15-25%.
- Safety: Autonomous systems and AI reduce human error by 20%.
- Transparency: Blockchain and IoT enhance supply chain visibility.
Challenges of Implementation
- High Costs: Digital transformation requires significant investment, challenging for SMEs.
- Regulatory Gaps: The IMO is developing frameworks, but regulations lag behind innovation.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity heightens vulnerability to attacks.
- Skill Gaps: The industry faces a shortage of tech-savvy professionals.
Future Outlook
The shipping industry is poised for further transformation. By 2030, autonomous ships could handle 10% of global trade, and green fuels may account for 30% of maritime energy. Digital twins and AI will drive predictive analytics, while blockchain will streamline global trade. Collaboration among stakeholders—shippers, ports, regulators, and tech providers—is crucial to overcome challenges and maximize benefits.
Chart: Future Shipping Ecosystem
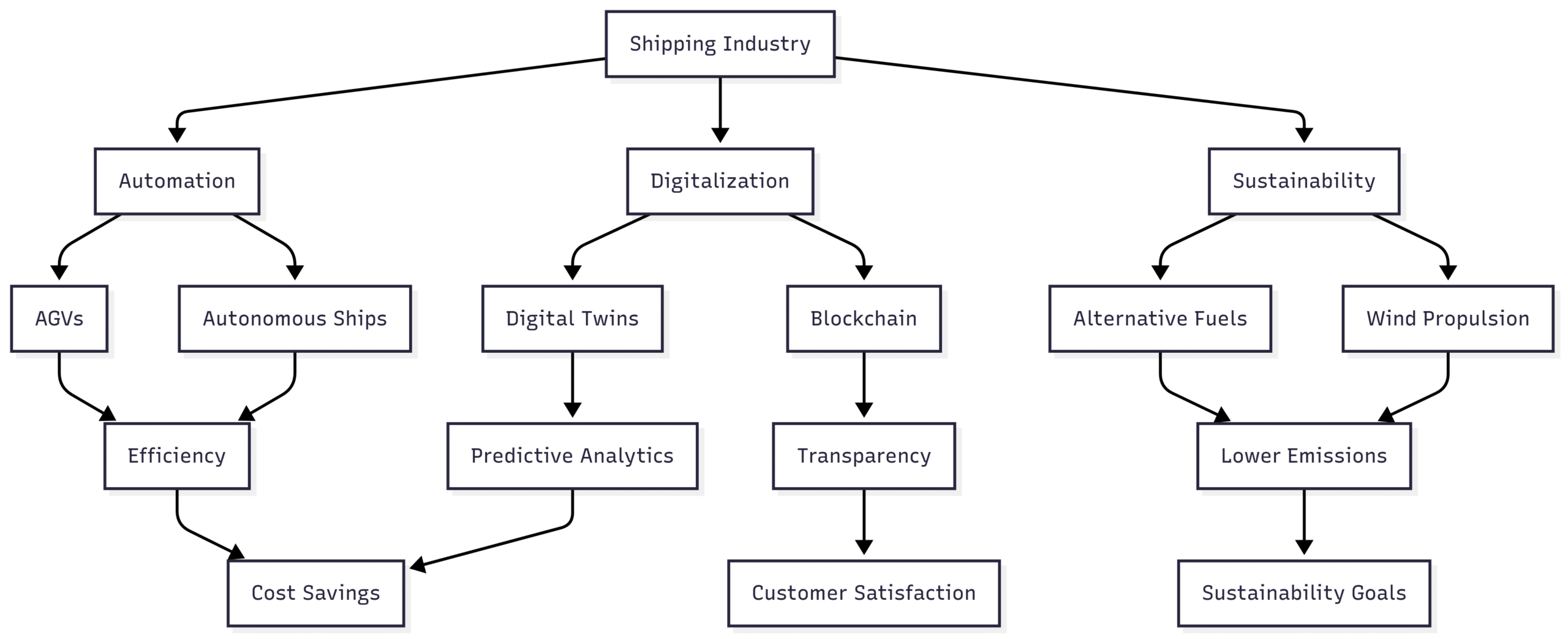
Conclusion
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the shipping industry, making it more efficient, sustainable, and resilient. From automation and AI to green fuels and blockchain, these innovations address critical challenges while unlocking new opportunities. However, success requires investment, regulatory alignment, and skilled talent. By embracing these technologies, the maritime sector can navigate toward a future that balances profitability with environmental responsibility, ensuring its vital role in global trade endures.
Happy Boating!
Share Technological Advancements in the Shipping Sector with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read SEEMP – Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan until we meet in the next article.
