Learn how to understand and maintain your marine oil pressure gauge to ensure your boat’s engine runs smoothly. Expert tips included!
Marine oil pressure gauges are vital tools for monitoring the health of a boat’s engine lubrication system. By providing real-time data on oil pressure, these gauges help prevent catastrophic engine damage, ensuring safe and efficient boating. This comprehensive guide explores how marine oil pressure gauges work, their importance, types, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, equipping boat owners with the knowledge to keep their engines running smoothly.
Why Marine Oil Pressure Gauges Matter
The oil pressure gauge is a critical component of any marine vessel, acting as an early warning system for engine issues. Insufficient oil pressure can lead to inadequate lubrication, causing excessive wear or complete engine failure. Conversely, high oil pressure may signal blockages or faulty components. Monitoring oil pressure allows boat operators to detect problems like leaking gaskets, broken hoses, or failing oil pumps before they escalate, saving time and costly repairs.
A marine oil pressure gauge measures the force with which oil circulates through the engine, typically displayed in PSI (pounds per square inch) or BAR. Normal oil pressure varies by engine type, but a general range of 25–65 PSI is considered healthy, with a rule of thumb being 10 PSI per 1,000 RPM. Understanding these readings ensures optimal engine performance and longevity.
How Marine Oil Pressure Gauges Work
Marine oil pressure gauges operate by measuring the resistance of oil within the engine’s lubrication system and converting it into a readable format. The process involves a sender unit, which detects oil pressure and transmits the signal to the gauge for display.
Key Components
- Sender Unit: Connected to the engine’s oil passage, the sender measures pressure changes. There are two types:
- American Sender: Higher resistance at lower pressure, decreasing as pressure rises.
- European Sender: Resistance increases with rising pressure.
- Gauge Display: Shows pressure readings on an analog dial or digital screen.
- Wiring: Connects the sender to the gauge, transmitting the signal.
The sender’s resistance changes based on oil pressure, which the gauge interprets and displays as PSI or BAR. Matching the sender type (American or European) to the gauge is crucial to avoid inaccurate readings.
Types of Marine Oil Pressure Gauges
Marine oil pressure gauges come in two primary types: mechanical and electronic (digital). Each has distinct features, advantages, and considerations.
Mechanical Oil Pressure Gauges
Mechanical gauges use a Bourdon tube to measure oil pressure directly. Oil is funneled into the tube, which expands under pressure, moving a needle on the gauge.
Advantages:
- Reliability: Simple design with no electrical dependency, functional even during power failures.
- Cost-Effective: Typically priced between $30–$60, depending on brand and features.
- Durability: Robust construction suits harsh marine environments.
Disadvantages:
- Less Precision: Slightly less accurate than digital gauges.
- Installation Complexity: Requires tubing to carry oil to the gauge, increasing installation effort.
Popular Models:
- VDO Vision Black 150-111: 0–150 PSI, 2 1/16″ diameter, $57.52.
- VDO Cockpit International 150-904: 0–150 PSI/0–10 BAR, $42.50.
Electronic (Digital) Oil Pressure Gauges
Digital gauges use a pressure sensor to measure oil pressure, displaying readings on an LCD screen. They rely on the boat’s electrical system for power.
Advantages:
- Precision: More accurate readings, ideal for high-performance engines.
- Features: Often include alarms, LED backlighting, and customizable displays.
- Ease of Installation: No oil tubing required, only electrical wiring.
Disadvantages:
- Power Dependency: Inoperable without electricity.
- Higher Cost: Prices range from $50–$125, depending on features.
Popular Models:
- VDO Cockpit Marine 110-11600 (4-in-1 Gauge): 0–80 PSI, includes water temperature, fuel level, and voltmeter, $125.62.
- VDO Cockpit Marine 110-15800: White dial, same specs as 110-11600, $125.62.
Comparison Table: Mechanical vs. Digital Gauges
| Feature | Mechanical Gauges | Digital Gauges |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Power Requirement | None | 12V Electrical |
| Price Range | $30–$60 | $50–$125 |
| Installation | Tubing + Wiring | Wiring Only |
| Features | Basic | Alarms, Backlighting |
| Durability | High | High (with IP65+ rating) |
Choosing the Best Marine Oil Pressure Gauge
Selecting the right gauge involves evaluating several factors to ensure compatibility, reliability, and usability.
Key Considerations
Display and Alerts:
- Opt for gauges with clear, backlit displays (LED preferred) for visibility in all lighting conditions.
- Warning lights or alarms for abnormal pressure readings enhance safety.
Resistance Type:
- Match the gauge to the sender (American: PSI, European: BAR) to ensure accurate readings.
- Indication ranges: 0–80/100 PSI (American) or 0–10 BAR (European).
Ingress Protection (IP Rating):
- Choose gauges with at least IP65 rating (dust-tight, water-jet resistant) or IP67 for submersion protection.
Brand Reputation:
- Trusted brands like VDO, Sierra, Faria, SeaStar, and Hardin offer reliable products with good support.
- VDO’s Cockpit Marine series is known for multifunctionality and durability.
Price:
- Budget-friendly mechanical gauges start at $30, while feature-rich digital gauges can cost up to $125.
- Consider long-term value over initial cost, as quality gauges reduce maintenance expenses.
Gauge Placement:
- Mount gauges where they’re easily visible from the helm and protected from direct water exposure.
- Ensure sufficient clearance for installation and maintenance.
Recommended Models with Specifications
| Model | Type | Scale | Diameter | Price | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDO 150-111 | Mechanical | 0–150 PSI | 2 1/16″ | $57.52 | IP64, U-bracket included |
| VDO 150-904 | Mechanical | 0–150 PSI/0–10 BAR | 2 1/16″ | $42.50 | IP64, flood lighting |
| VDO 110-11600 (4-in-1) | Digital | 0–80 PSI | 3 3/8″ | $125.62 | Black dial, chrome bezel |
| VDO 110-15800 (4-in-1) | Digital | 0–80 PSI | 3 3/8″ | $125.62 | White dial, multifunction |
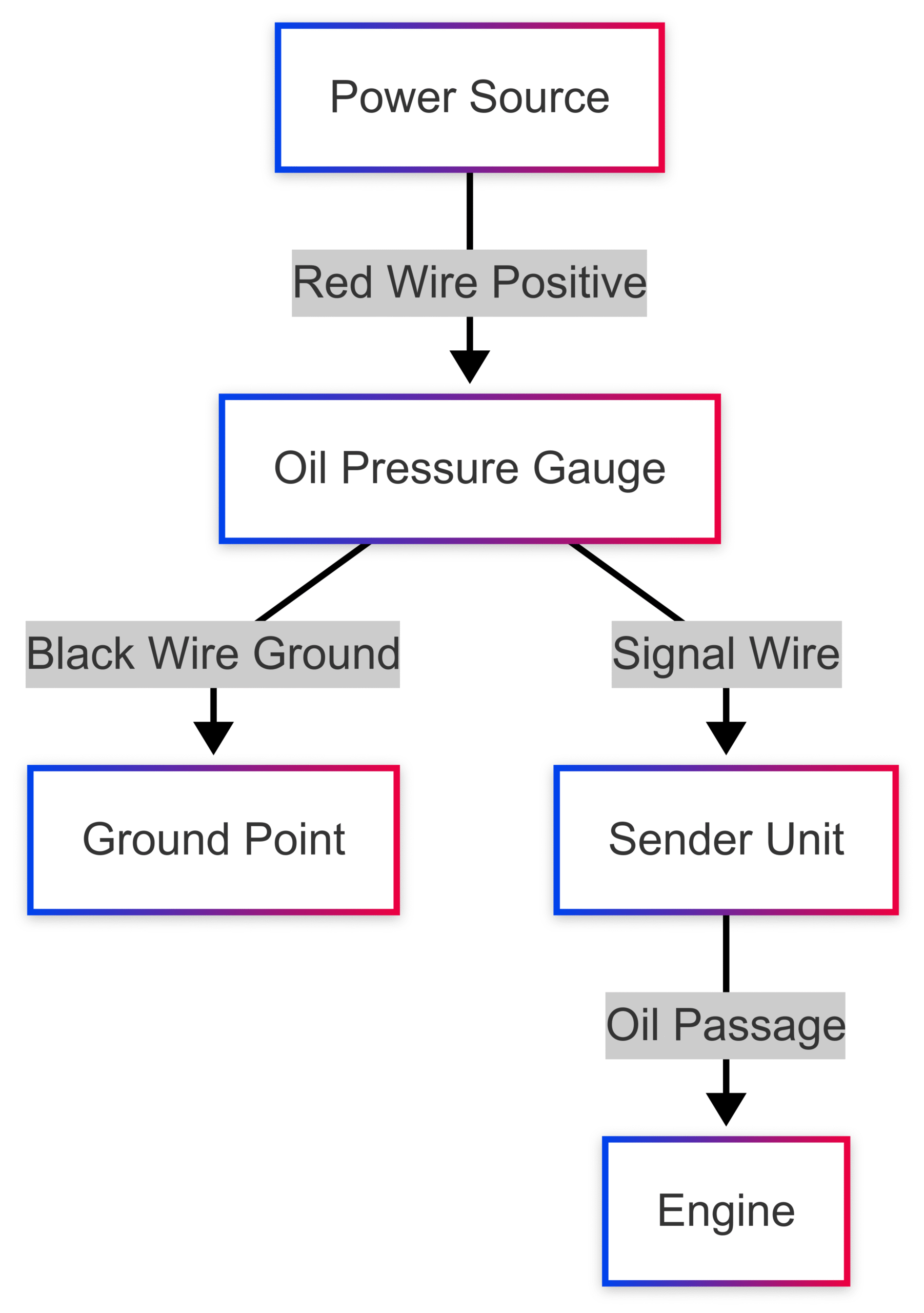
Installation of Marine Oil Pressure Gauges
Proper installation ensures accurate readings and reliable performance. Below is a step-by-step guide for installing a marine oil pressure gauge.
Tools and Materials
- Marine oil pressure gauge kit (gauge, sender, bracket, wires, nuts, washers).
- Screwdriver, wrench, and wire strippers.
- Electrical tape or heat-shrink tubing for insulation.
- Resistors (47-ohm, 100-ohm) for testing.
Installation Steps
Choose Mounting Location:
- Select a spot on the dashboard or helm with clear visibility and sufficient clearance.
- Ensure the location is protected from water and vibration.
Mount the Gauge:
- Secure the bracket to the panel using provided nuts and washers.
- Attach the gauge to the bracket, ensuring a firm connection.
Connect the Sender:
- Install the sender unit in the engine’s oil passage, following manufacturer instructions.
- Connect the sender to the gauge using provided wires, ensuring secure and insulated connections.
Wire the Gauge:
- Run the power cable from the gauge to the boat’s power source.
- Connect the red wire (positive) to the power source and the black wire (ground) to a grounding point.
- For dual-station setups, connect both gauges to the same sender, as advised by Hatteras yacht owners on forums.
Test the Gauge:
- Use a 47-ohm resistor to simulate 40 PSI and a 100-ohm resistor for 80 PSI.
- Power the gauge and verify the needle moves to the correct position.
- If readings are incorrect, check wiring and sender connections.
Wiring Diagram (Chart)
Testing and Calibration
Regular testing ensures the gauge provides accurate readings. Follow these steps to test your gauge:
Simulate Pressure:
- Disconnect the sender wire and connect a 47-ohm or 100-ohm resistor between the signal input and ground.
- Power the gauge and observe the needle: 47-ohm ≈ 40 PSI, 100-ohm ≈ 80 PSI.
Verify Wiring:
- If the needle doesn’t move correctly, inspect all connections, especially the sender and ground.
- Ensure no loose wires or corrosion.
Calibrate if Needed:
- Some digital gauges allow calibration via settings. Refer to the manufacturer’s manual.
- Mechanical gauges may require professional recalibration if consistently inaccurate.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of your marine oil pressure gauge and ensures reliable performance.
- Check Oil Levels: Regularly verify engine oil levels and condition to prevent low pressure issues.
- Inspect Gauge and Sender: Look for corrosion, loose connections, or physical damage.
- Clean the Gauge: Use a soft cloth to clean the lens, avoiding abrasive materials that could scratch it.
- Protect from Elements: Ensure the gauge’s IP rating (IP65 or higher) matches the marine environment.
- Schedule Calibration: Test and calibrate gauges annually or per manufacturer recommendations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Marine oil pressure gauges can encounter issues that affect their performance. Below are common problems and solutions.
High Oil Pressure
- Symptoms: Readings consistently above 65 PSI.
- Causes: Faulty pressure relief valve, blocked oil lines, or overly thick oil.
- Solutions:
- Inspect and replace the pressure relief valve if stuck.
- Check oil lines for blockages and clear them.
- Ensure the correct oil viscosity is used.
Low Oil Pressure
- Symptoms: Readings below 25 PSI or fluctuating.
- Causes: Low oil level, failing oil pump, or faulty sender.
- Solutions:
- Check and top up oil levels.
- Test the oil pump for proper function.
- Replace the sender if defective.
Gauge Malfunction
- Symptoms: Erratic readings, stuck needle, or no response.
- Causes: Faulty gauge, wiring issues, or sender failure.
- Solutions:
- Verify wiring connections and insulation.
- Test the gauge with resistors to isolate the issue.
- Replace the gauge or sender if confirmed faulty.
Real-World Example: Hatteras Yacht Forum
A Hatteras yacht owner reported incorrect oil pressure readings after installing gauges in the engine room. The issue stemmed from mismatched sender types and improper wiring. By using a dual-station sender and confirming connections (I=ignition, S=sender, G=ground), the owner resolved the problem, highlighting the importance of matching components and thorough testing.
Are Marine Oil Pressure Gauges Worth It?
Marine oil pressure gauges are an essential investment for any boat owner. They provide critical insights into engine health, preventing costly damage by detecting issues early. Whether choosing a mechanical gauge for simplicity or a digital gauge for precision, the benefits outweigh the cost, which ranges from $30 to $125 for quality models.
Beyond functionality, modern gauges enhance the dashboard’s aesthetic, with sleek designs and customizable options. Brands like VDO offer multifunction gauges that combine oil pressure with other metrics, reducing clutter and improving usability. For vessels operating in harsh marine environments, gauges with high IP ratings ensure durability and reliability.
Advanced Options: Multifunction and Custom Gauges
For boaters seeking a streamlined dashboard, multifunction gauges combine oil pressure with metrics like water temperature, fuel level, and voltage. VDO’s Cockpit Marine 4-in-1 gauges are a popular choice, offering a compact solution without sacrificing readability.
Custom gauges allow for tailored solutions, blending analog and digital inputs (e.g., CANbus and traditional senders). These are ideal for older vessels with mechanical engines or owners desiring a specific aesthetic, such as brushed aluminum bezels or logo-embossed displays.
Benefits of Digital Multifunction Gauges
- Compact Design: Displays multiple metrics on one screen.
- Real-Time Data: More accurate and faster updates than analog gauges.
- Customizable: Adjust display settings to prioritize key metrics.
- Durability: High-quality materials and IP67 ratings resist marine conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding your marine oil pressure gauge is crucial for maintaining your boat’s engine health and ensuring safe voyages. By selecting the right gauge, installing it correctly, and performing regular maintenance, you can prevent engine issues and extend your vessel’s lifespan. Whether you prefer the simplicity of mechanical gauges or the precision of digital models, investing in a quality marine oil pressure gauge is a decision that pays dividends in reliability and peace of mind.
For boaters upgrading their vessels or troubleshooting existing gauges, brands like VDO, Sierra, and Faria offer reliable options tailored to marine environments. With proper care, your oil pressure gauge will keep you informed and your engine running smoothly for years to come.
Happy Boating!
Share Guide to Understanding Your Marine Oil Pressure Gauge with your friends and leave a comment below with your thoughts.
Read Boat Barbecue Grills for Convenient Cooking on the Water until we meet in the next article.
